Page 105 - untitled
P. 105
AAAC46 21/5/05 10:53 AM Page 104
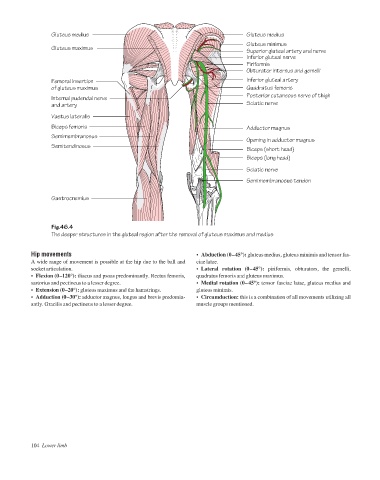
Gluteus medius
Gluteus medius
Gluteus minimus
Gluteus maximus
Superior gluteal artery and nerve
Inferior gluteal nerve
Piriformis
Obturator internus and gemelli
Femoral insertion Inferior gluteal artery
of gluteus maximus Quadratus femoris
Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh
Internal pudendal nerve
and artery Sciatic nerve
Vastus lateralis
Biceps femoris Adductor magnus
Semimembranosus
Opening in adductor magnus
Semitendinosus
Biceps (short head)
Biceps (long head)
Sciatic nerve
Semimembranosus tendon
Gastrocnemius
Fig.46.4
The deeper structures in the gluteal region after the removal of gluteus maximus and medius
Hip movements • Abduction (0–45°): gluteus medius, gluteus minimis and tensor fas-
A wide range of movement is possible at the hip due to the ball and ciae latae.
socket articulation. • Lateral rotation (0–45°): piriformis, obturators, the gemelli,
• Flexion (0–120°): iliacus and psoas predominantly. Rectus femoris, quadratus femoris and gluteus maximus.
sartorius and pectineus to a lesser degree. • Medial rotation (0–45°): tensor fasciae latae, gluteus medius and
• Extension (0–20°): gluteus maximus and the hamstrings. gluteus minimis.
• Adduction (0–30°): adductor magnus, longus and brevis predomin- • Circumduction: this is a combination of all movements utilizing all
antly. Gracilis and pectineus to a lesser degree. muscle groups mentioned.
104 Lower limb