Page 350 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 350
326 Risk Stratification in Asymptomatic Diabetics :Role Of Selective
Imaging With Cardiac CT And Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
the necessity to define the cardiovascular risk in the and to determine its association with myocardial per-
asymptomatic diabetic population who could benefit fusion abnormalities (Anand et al.)(Ref 4)
from this screening. Due to the high rate of cardio- (figure-1).
vascular mortality and morbidity in the type-2 diabet-
ic population, there has been considerable interest
in establishing the incidence of subclinical or occult
CAD and the factors influencing it. The exercise-ECG
has poor accuracy for detecting CAD in asymptomat-
ic diabetic patients. Though the DIAD study investiga-
tors reported a 20% prevalence of silent myocardial
ischemia in a large asymptomatic diabetic cohort
(n=1123) using SPECT imaging, this was not a cost-ef-
fective method for screening large populations.
Improvements in risk stratification by
imaging subclinical atherosclerosis
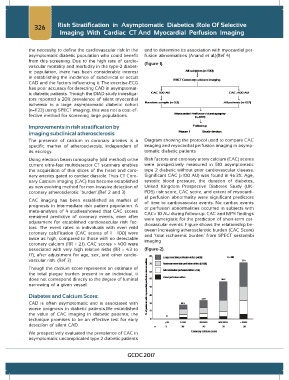
The presence of calcium in coronary arteries is a Diagram showing the protocol used to compare CAC
specific marker of atherosclerosis, independent of imaging and myocardial perfusion imaging in asymp-
its etiology. tomatic diabetic patients
Using electron beam tomography (old method) orthe Risk factors and coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores
current ultra-fast multidetector CT scanners enables were prospectively measured in 510 asymptomatic
the acquisition of thin slices of the heart and coro- type 2 diabetic without prior cardiovascular disease.
nary arteries gated to cardiac diastole. Thus CT Coro- Significant CAC (>100 AU) was found in 46.3%. Age,
nary Calcium Imaging (CAC) has become established systolic blood pressure, the duration of diabetes,
as new evolving method for non-invasive detection of United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UK-
coronary atherosclerotic ‘burden’.(Ref 2 and 3) PDS) risk score, CAC score, and extent of myocardi-
al perfusion abnormality were significant predictors
CAC imaging has been established as marker of of time to cardiovascular events. No cardiac events
prognosis in intermediate risk patient population. A or perfusion abnormalities occurred in subjects with
meta-analysis of 4 studiesshowed that CAC scores CAC< 10 AU during follow-up. CAC and MPS findings
remained predictive of coronary events, even after were synergistic for the prediction of short-term car-
adjustment for established cardiovascular risk fac- diovascular events. Figure shows the relationship be-
tors. The event rates in individuals with even mild tween increasing atherosclerotic burden (CAC Score)
coronary calcification (CAC scores of 1 – 100) were and ‘total ischaemic burden’ from SPECT sestamibi
twice as high, compared to those with no detectable imaging
coronary calcium (RR = 2.1). CAC scores > 400 were
associated with very high relative risks (RR = 4.3 to (figure-2).
17), after adjustment for age, sex, and other cardio-
vascular risk. (Ref 3)
Though the calcium score represents an estimate of
the total plaque burden present in an individual, it
does not correspond directly to the degree of luminal
narrowing of a given vessel.
Diabetes and Calcium Score:
CAD is often asymptomatic and is associated with
worse prognosis in diabetic patients.We established
the value of CAC imaging in diabetic patients, the
technique promises to be an effective test for early
detection of silent CAD.
We prospectively evaluated the prevalence of CAC in
asymptomatic uncomplicated type 2 diabetic patients
GCDC 2017