Page 484 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 484
Heart Failure: Drug Thaerapies &
460 Revascularization Strategies
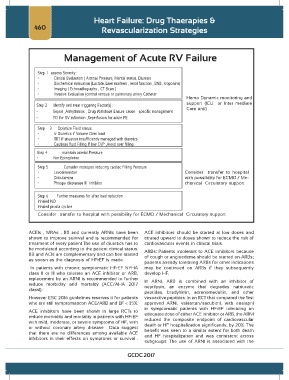
Management of Acute RV Failure
Step 1 assess Severity :
• Clinical Evaluation ( Arterial Pressure, Mental status, Diuresis
• Biochemical evaluation (Lactate, Liver markers , renal function , BNB , troponins)
• Imaging ( Echocadiography , CT Scan )
• Invasive Evaluation (central venous or pulmonary artery Catheter
Hemo Dynamic monitoring and
support (ICU or Inter mediate
Step 2 Identify and treat triggering Factor(s) :
• Sepsis ,Arrhythmias , Drug Withdrawl Ensure cause – specific management Care unit)
• PCI for RV infarction ,Reperfusion for acute PE
Step 3 Optimize Fluid status
• Iv Diuretics if Volume Over load
• RRT if situation insufficiently managed with diuretics
• Cautious fluid Filling If low CVP ,Avoid over filling
Step 4 maintain arterial Pressure
• Nor Epinephrine
Step 5 Consider inotropes reducing cardiac Filling Pressure
• Levosimendan Consider transfer to hospital
• Dobutamine with possibility for ECMO / Me-
• Phospo diestarase III Inhibitor chanical Circulatory support
Step 6 Further measures for after load reduction
Inhaled NO
Inhaled prosta cycline
Consider transfer to hospital with possibility for ECMO / Mechanical Circulatory support
ACEIs , MRAs , BB and currently ARNIs have been ACE inhibitors should be started at low doses and
shown to improve survival and is recommended for titrated upward to doses shown to reduce the risk of
treatment of every patient.The use of diuretics has to cardiovascular events in clinical trials.
be modulated according to the patient clinical status. ARBs: Patients intolerant to ACE inhibitors because
BB and ACIs are complementary and can bee started of cough or angioedema should be started on ARBs;
as soosn as the diagnosis of HFrEF is made.
patients already tolerating ARBs for other indications
In patients with chronic symptomatic HFrEF NYHA may be continued on ARBs if they subsequently
class II or III who tolerate an ACE inhibitor or ARB, develop HF.
replacement by an ARNI is recommended to further In ARNI, ARB is combined with an inhibitor of
reduce morbidity and mortality (ACC/AHA 2017 neprilysin, an enzyme that degrades natriuretic
classI).
peptides, bradykinin, adrenomedullin, and other
However ESC 2016 guidelines reserves it for patients vasoactive peptides. In an RCT that compared the first
who are still symptomaticon ACE/ARB and EF < 35%. approved ARNI, valsartan/sacubitril, with enalapril
in symptomatic patients with HFrEF tolerating an
ACE inhibitors have been shown in large RCTs to
reduce morbidity and mortality in patients with HFrEF adequate dose of either ACE inhibitor or ARB, the ARNI
with mild, moderate, or severe symptoms of HF, with reduced the composite endpoint of cardiovascular
or without coronary artery disease . Data suggest death or HF hospitalization significantly, by 20%. The
that there are no differences among available ACE benefit was seen to a similar extent for both death
inhibitors in their effects on symptoms or survival . and HF hospitalization and was consistent across
subgroups. The use of ARNI is associated with the
GCDC 2017