Page 308 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 308
Chapter 6 CARE OF THE TRAUMATIZED PATIENT 293
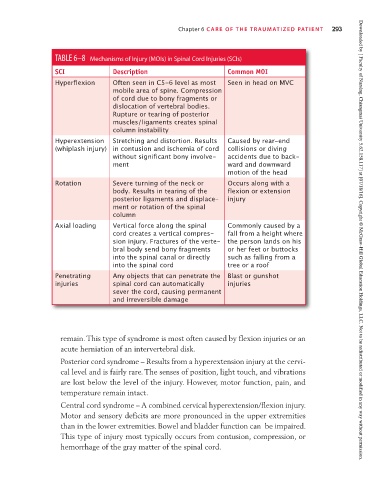
TABLE 6–8 Mechanisms of Injury (MOIs) in Spinal Cord Injuries (SCIs)
SCI Description Common MOI
Hyperflexion Often seen in C5-6 level as most Seen in head on MVC
mobile area of spine. Compression
of cord due to bony fragments or
dislocation of vertebral bodies.
Rupture or tearing of posterior
muscles/ligaments creates spinal
column instability
Hyperextension Stretching and distortion. Results Caused by rear-end
(whiplash injury) in contusion and ischemia of cord collisions or diving
without significant bony involve- accidents due to back-
ment ward and downward
motion of the head
Rotation Severe turning of the neck or Occurs along with a
body. Results in tearing of the flexion or extension
posterior ligaments and displace- injury
ment or rotation of the spinal
column
Axial loading Vertical force along the spinal Commonly caused by a
cord creates a vertical compres- fall from a height where
sion injury. Fractures of the verte- the person lands on his Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
bral body send bony fragments or her feet or buttocks
into the spinal canal or directly such as falling from a
into the spinal cord tree or a roof
Penetrating Any objects that can penetrate the Blast or gunshot
injuries spinal cord can automatically injuries
sever the cord, causing permanent
and irreversible damage
remain. This type of syndrome is most often caused by flexion injuries or an
acute herniation of an intervertebral disk.
Posterior cord syndrome – Results from a hyperextension injury at the cervi-
cal level and is fairly rare. The senses of position, light touch, and vibrations
are lost below the level of the injury. However, motor function, pain, and
temperature remain intact.
Central cord syndrome – A combined cervical hyperextension/flexion injury.
Motor and sensory deficits are more pronounced in the upper extremities
than in the lower extremities. Bowel and bladder function can be impaired.
This type of injury most typically occurs from contusion, compression, or
hemorrhage of the gray matter of the spinal cord.