Page 1493 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1493
1468 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 89: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Related Disorders 1469
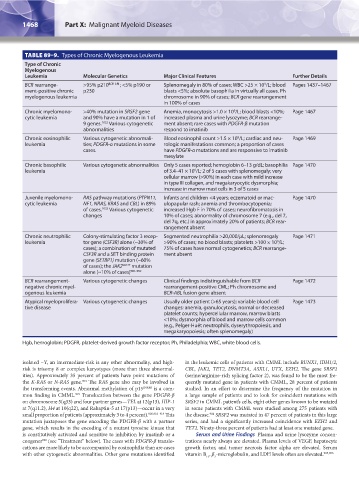
TABLE 89–9. Types of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Type of Chronic
Myelogenous
Leukemia Molecular Genetics Major Clinical Features Further Details
BCR rearrange- >95% p210 BCR-ABL ; <5% p190 or Splenomegaly in 80% of cases; WBC >25 × 10 /L; blood Pages 1437–1467
9
ment-positive chronic p230 blasts <5%; absolute basophilia in virtually all cases. Ph
myelogenous leukemia chromosome in 90% of cases; BCR gene rearrangement
in 100% of cases
Chronic myelomono- >40% mutation in SRSF2 gene Anemia, monocytosis >1.0 × 10 /L; blood blasts <10%; Page 1467
9
cytic leukemia and 90% have a mutation in 1 of increased plasma and urine lysozyme; BCR rearrange-
9 genes. 1032 Various cytogenetic ment absent; rare cases with PDGFR-β mutation
abnormalities respond to imatinib
Chronic eosinophilic Various cytogenetic abnormali- Blood eosinophil count >1.5 × 10 /L; cardiac and neu- Page 1469
9
leukemia ties; PDGFR-α mutations in some rologic manifestations common; a proportion of cases
cases. have PDGFR-α mutations and are responsive to imatinib
mesylate
Chronic basophilic Various cytogenetic abnormalities Only 5 cases reported; hemoglobin 6–13 g/dL; basophilia Page 1470
leukemia of 3.4–41 × 10 /L; 2 of 5 cases with splenomegaly; very
9
cellular marrow (>90%) in each case with mild increase
in type III collagen, and megakaryocytic dysmorphia;
increase in marrow mast cells in 3 of 5 cases
Juvenile myelomono- RAS pathway mutations (PTPN11, Infants and children <4 years; eczematoid or mac- Page 1470
cytic leukemia NF1, NRAS, KRAS and CBL) in 89% ulopapular rash; anemia and thrombocytopenia;
of cases. 1033 Various cytogenetic increased Hgb F in 70% of cases; neurofibromatosis in
changes 10% of cases; abnormality of chromosome 7 (e.g., del 7,
del 7q, etc.) in approximately 20% of patients; BCR rear-
rangement absent
Chronic neutrophilic Colony-stimulating factor 3 recep- Segmented neutrophilia >20,000/μL; splenomegaly Page 1471
leukemia tor gene (CSF3R) alone (~30% of >90% of cases; no blood blasts; platelets >100 × 10 /L;
9
cases); a combination of mutated 75% of cases have normal cytogenetics; BCR rearrange-
CSF3R and a SET binding protein ment absent
gene (SETBP1) mutation (~60%
of cases); the JAK2 V617F mutation
alone (~10% of cases) 990–992
BCR rearrangement- Various cytogenetic changes Clinical findings indistinguishable from BCR Page 1472
negative chronic myel- rearrangement-positive CML; Ph chromosome and
ogenous leukemia BCR-ABL fusion gene absent
Atypical myeloprolifera- Various cytogenetic changes Usually older patient (>65 years); variable blood cell Page 1473
tive disease changes: anemia, granulocytosis, normal or decreased
platelet counts; hypercellular marrow, marrow blasts
<10%; dysmorphia of blood and marrow cells common
(e.g., Pelger-Huët neutrophils, dyserythropoiesis, and
megakaryopoiesis; often splenomegaly)
Hgb, hemoglobin; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; Ph, Philadelphia; WBC, white blood cells.
isolated −Y, an intermediate-risk is any other abnormality, and high- in the leukemic cells of patients with CMML include RUNX1, IDH1/2,
risk is trisomy 8 or complex karyotypes (more than three abnormal- CBL, JAK2, TET2, DNMT3A, ASXL1, UTX, EZH2. The gene SRSF2
ities). Approximately 35 percent of patients have point mutations of (serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 2), was found to be the most fre-
the K-RAS or N-RAS gene. The RAS gene also may be involved in quently mutated gene in patients with CMML, 28 percent of patients
904
the transforming events. Abnormal methylation of p15 INK4B is a com- studied. In an effort to determine the frequency of the mutation in
mon finding in CMML. Translocation between the gene PDGFR-β a large sample of patients and to look for coincident mutations with
915
on chromosome 5(q33) and four partner genes—TEL at 12(p13), HIP-1 SRSF2 in CMML patient’s cells, eight other genes known to be mutated
at 7(q11.2), H4 at 10(q22), and Rabaptin-5 at 17(p13)—occur in a very in some patients with CMML were studied among 275 patients with
small proportion of patients (approximately 3 to 4 percent). 905,916–919 This the disease. SRSF2 was mutated in 47 percent of patients in this large
904
mutation juxtaposes the gene encoding the PDGFR-β with a partner series, and had a significantly increased coincidence with EZH2 and
gene, which results in the encoding of a mutant tyrosine kinase that TET2. Ninety-three percent of patients had at least one mutated gene.
is constitutively activated and sensitive to inhibition by imatinib or a Serum and Urine Findings Plasma and urine lysozyme concen-
congener (see “Treatment” below). The cases with PDGFR-β translo- trations nearly always are elevated. Plasma levels of VEGF, hepatocyte
920
cations are more likely to be accompanied by eosinophilia than are cases growth factor, and tumor necrosis factor alpha are elevated. Serum
with other cytogenetic abnormalities. Other gene mutations identified vitamin B , β -microglobulin, and LDH levels often are elevated. 905,906
12 2
Kaushansky_chapter 89_p1437-1490.indd 1468 9/18/15 3:42 PM