Page 1045 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1045
1008 Part seven Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
$ % &
1RUPDO GXRGHQXP &HOLDF GLVHDVH GXRGHQXP &HOLDF GLVHDVH &' VWDLQ
' ( )
&URKQ¶V GLVHDVH FRORQ 8OFHUDWLYH FROLWLV &9,' HQWHURSDWK\
GXRGHQXP
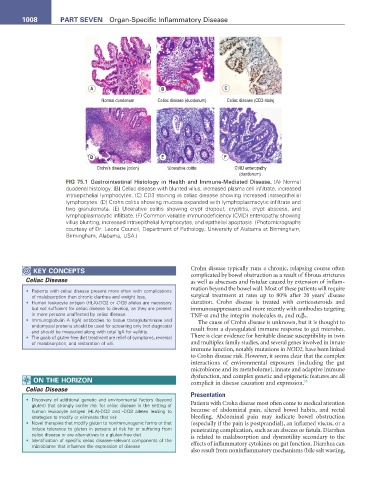
FIG 75.1 Gastrointestinal Histology in Health and Immune-Mediated Disease. (A) Normal
duodenal histology. (B) Celiac disease with blunted villus, increased plasma cell infiltrate, increased
intraepithelial lymphocytes. (C) CD3 staining in celiac disease showing increased intraepithelial
lymphocytes. (D) Crohn colitis showing mucosa expanded with lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and
two granulomata. (E) Ulcerative colitis showing crypt dropout, cryptitis, crypt abscess, and
lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. (F) Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) enteropathy showing
villus blunting, increased intraepithelial lymphocytes, and epithelial apoptosis. (Photomicrographs
courtesy of Dr. Leona Council, Department of Pathology, University of Alabama at Birmingham,
Birmingham, Alabama, USA.)
KeY COnCePts Crohn disease typically runs a chronic, relapsing course often
Celiac Disease complicated by bowel obstruction as a result of fibrous strictures
as well as abscesses and fistulae caused by extension of inflam-
• Patients with celiac disease present more often with complications mation beyond the bowel wall. Most of these patients will require
of malabsorption than chronic diarrhea and weight loss. surgical treatment at rates up to 80% after 20 years’ disease
• Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DQ2 or -DQ8 alleles are necessary duration. Crohn disease is treated with corticosteroids and
but not sufficient for celiac disease to develop, as they are present immunosuppressants and more recently with antibodies targeting
in more persons unaffected by celiac disease. TNF-α and the integrin molecules α 4 and α 4 β 7 .
• Immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies to tissue transglutaminase and The cause of Crohn disease is unknown, but it is thought to
endomysial proteins should be used for screening only (not diagnosis) result from a dysregulated immune response to gut microbes.
and should be measured along with total IgA for validity.
• The goals of gluten-free diet treatment are relief of symptoms, reversal There is clear evidence for heritable disease susceptibility in twin
of malabsorption, and restoration of villi. and multiplex family studies, and several genes involved in innate
immune function, notably mutations in NOD2, have been linked
to Crohn disease risk. However, it seems clear that the complex
interactions of environmental exposures (including the gut
microbiome and its metabolome), innate and adaptive immune
On tHe HOrIZOn dysfunction, and complex genetic and epigenetic features are all
25
complicit in disease causation and expression.
Celiac Disease
Presentation
• Discovery of additional genetic and environmental factors (beyond
gluten) that strongly confer risk for celiac disease in the setting of Patients with Crohn disease most often come to medical attention
human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DQ2 and -DQ8 alleles leading to because of abdominal pain, altered bowel habits, and rectal
strategies to modify or eliminate that risk bleeding. Abdominal pain may indicate bowel obstruction
• Novel therapies that modify gluten to nonimmunogenic forms or that (especially if the pain is postprandial), an inflamed viscus, or a
induce tolerance to gluten in persons at risk for or suffering from penetrating complication, such as an abscess or fistula. Diarrhea
celiac disease or are alternatives to a gluten-free diet is related to malabsorption and dysmotility secondary to the
• Identification of specific celiac disease–relevant components of the
microbiome that influence the expression of disease effects of inflammatory cytokines on gut function. Diarrhea can
also result from noninflammatory mechanisms (bile salt wasting,