Page 234 - 9 teachers social book 9 @ 2077 ctp_Neat
P. 234
fall in this region. The Great Dividing Range is also called Blue Mountains in New
South Wales. These ranges include the New England Plateaus, the Australian Alps,
the Snowy Mountains, Blue Mountains and the Grampian Mountains. These landforms
were made due to uplifting, folding and volcanic processes in the Earth’s Crust.
Australia’s highest peak Mt Kosciusko (2228m) is situated in New South Wales in
this region.
Western Plateau
The western plateau is a low, flat area that has been eroded over a period of millions
of years. There are many deserts in the western plateau. This region is very dry due
to cold water currents off the coast of Western Australia. Some of the deserts in this
region are the Gibson, Tanami, Canning, Great Sandy and Great Victoria Desert.
This region is rich for goldmines. The land in this region is not completely flat. It has
some very low ranges but the maximum height is less than 500 m from the sea level.
The western plateau is covered with sandy desert. The Pilbara, Arnhem land and
Kimberly Plateaus are also high points in this area.
Central Lowland
The central lowlands are dry because rainfall is obstructed by the Eastern Highlands.
It is a huge mass of old ancient crystalline rocks covering nearly two third of Australia.
The Simpson Desert, which extends for 170,000 sq. km is in the central lowlands. The
desert is popular for its Red Sanddunes extending north to south. The Lake Eyre is
the largest salt lake in Australia found in the Simpson Desert. The Lake Eyre is the
largest lake as well as the lowest point on the Australian mainland at15 m below the
sea level.
The Flinder Range in South Australia extends for 800 km and is located about 1100 km
north to Adelaide. Its tallest peak is St. Mary Peak is 1171m tall. The River Murray
and its tributaries mainly the Darling is called together as the Murray Darling.
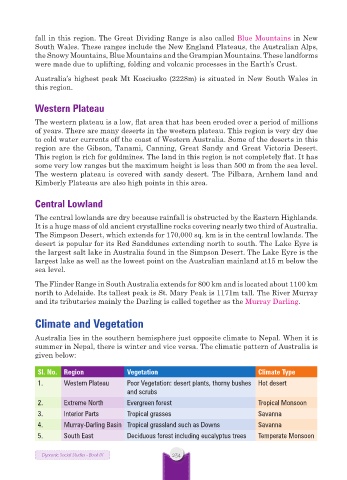
Climate and Vegetation
Australia lies in the southern hemisphere just opposite climate to Nepal. When it is
summer in Nepal, there is winter and vice versa. The climatic pattern of Australia is
given below:
Sl. No. Region Vegetation Climate Type
1. Western Plateau Poor Vegetation: desert plants, thorny bushes Hot desert
and scrubs
2. Extreme North Evergreen forest Tropical Monsoon
3. Interior Parts Tropical grasses Savanna
4. Murray-Darling Basin Tropical grassland such as Downs Savanna
5. South East Deciduous forest including eucalyptus trees Temperate Monsoon
Dynamic Social Studies - Book IX 234