Page 199 - Health, Population and Environment Education 10
P. 199
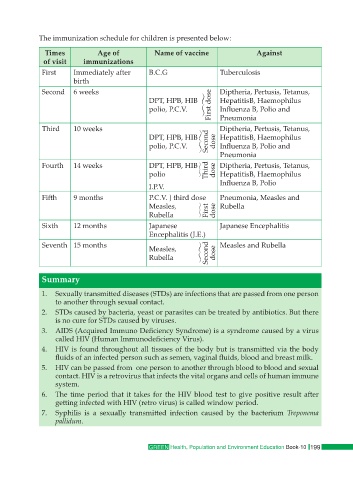
The immunization schedule for children is presented below:
Times Age of Name of vaccine Against
of visit immunizations
First Immediately after B.C.G Tuberculosis
birth
Second 6 weeks Diptheria, Pertusis, Tetanus,
DPT, HPB, HIB HepatitisB, Haemophilus
polio, P.C.V. First dose Influenza B, Polio and
Pneumonia
Third 10 weeks Diptheria, Pertusis, Tetanus,
DPT, HPB, HIB Second HepatitisB, Haemophilus
polio, P.C.V. dose Influenza B, Polio and
Pneumonia
Fourth 14 weeks DPT, HPB, HIB Diptheria, Pertusis, Tetanus,
polio Third dose HepatitisB, Haemophilus
I.P.V. Influenza B, Polio
Fifth 9 months P.C.V. } third dose Pneumonia, Measles and
Measles, Rubella
Rubella First dose
Sixth 12 months Japanese Japanese Encephalitis
Encephalitis (J.E.)
Seventh 15 months Measles, Measles and Rubella
Rubella Second dose
Summary
1. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are passed from one person
to another through sexual contact.
2. STDs caused by bacteria, yeast or parasites can be treated by antibiotics. But there
is no cure for STDs caused by viruses.
3. AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) is a syndrome caused by a virus
called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
4. HIV is found throughout all tissues of the body but is transmitted via the body
fluids of an infected person such as semen, vaginal fluids, blood and breast milk.
5. HIV can be passed from one person to another through blood to blood and sexual
contact. HIV is a retrovirus that infects the vital organs and cells of human immune
system.
6. The time period that it takes for the HIV blood test to give positive result after
getting infected with HIV (retro virus) is called window period.
7. Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema
pallidum.
GREEN Health, Population and Environment Education Book-10 199