Page 10 - PNEUMONIA NURSING CARE PLAN
P. 10
CikguOnline
CikguOnline
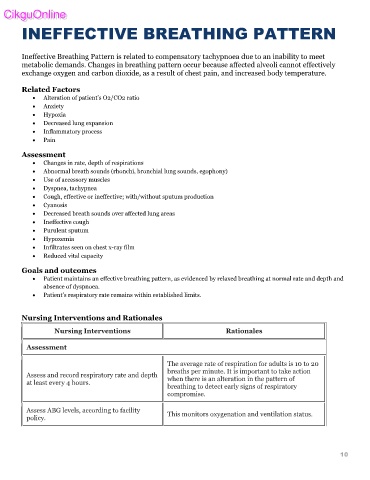
INEFFECTIVE BREATHING PATTERN
Ineffective Breathing Pattern is related to compensatory tachypnoea due to an inability to meet
metabolic demands. Changes in breathing pattern occur because affected alveoli cannot effectively
exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide, as a result of chest pain, and increased body temperature.
Related Factors
• Alteration of patient’s O2/CO2 ratio
• Anxiety
• Hypoxia
• Decreased lung expansion
• Inflammatory process
• Pain
Assessment
• Changes in rate, depth of respirations
• Abnormal breath sounds (rhonchi, bronchial lung sounds, egophony)
• Use of accessory muscles
• Dyspnea, tachypnea
• Cough, effective or ineffective; with/without sputum production
• Cyanosis
• Decreased breath sounds over affected lung areas
• Ineffective cough
• Purulent sputum
• Hypoxemia
• Infiltrates seen on chest x-ray film
• Reduced vital capacity
Goals and outcomes
• Patient maintains an effective breathing pattern, as evidenced by relaxed breathing at normal rate and depth and
absence of dyspnoea.
• Patient’s respiratory rate remains within established limits.
Nursing Interventions and Rationales
Nursing Interventions Rationales
Assessment
The average rate of respiration for adults is 10 to 20
breaths per minute. It is important to take action
Assess and record respiratory rate and depth when there is an alteration in the pattern of
at least every 4 hours.
breathing to detect early signs of respiratory
compromise.
Assess ABG levels, according to facility This monitors oxygenation and ventilation status.
policy.
10