Page 4 - PNEUMONIA NURSING CARE PLAN
P. 4
CikguOnline
CikguOnline
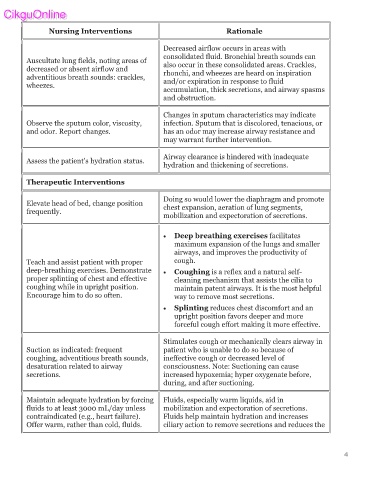
Nursing Interventions Rationale
Decreased airflow occurs in areas with
consolidated fluid. Bronchial breath sounds can
Auscultate lung fields, noting areas of also occur in these consolidated areas. Crackles,
decreased or absent airflow and
adventitious breath sounds: crackles, rhonchi, and wheezes are heard on inspiration
and/or expiration in response to fluid
wheezes.
accumulation, thick secretions, and airway spasms
and obstruction.
Changes in sputum characteristics may indicate
Observe the sputum color, viscosity, infection. Sputum that is discolored, tenacious, or
and odor. Report changes. has an odor may increase airway resistance and
may warrant further intervention.
Airway clearance is hindered with inadequate
Assess the patient’s hydration status.
hydration and thickening of secretions.
Therapeutic Interventions
Doing so would lower the diaphragm and promote
Elevate head of bed, change position chest expansion, aeration of lung segments,
frequently.
mobilization and expectoration of secretions.
• Deep breathing exercises facilitates
maximum expansion of the lungs and smaller
airways, and improves the productivity of
Teach and assist patient with proper cough.
deep-breathing exercises. Demonstrate • Coughing is a reflex and a natural self-
proper splinting of chest and effective cleaning mechanism that assists the cilia to
coughing while in upright position. maintain patent airways. It is the most helpful
Encourage him to do so often. way to remove most secretions.
• Splinting reduces chest discomfort and an
upright position favors deeper and more
forceful cough effort making it more effective.
Stimulates cough or mechanically clears airway in
Suction as indicated: frequent patient who is unable to do so because of
coughing, adventitious breath sounds, ineffective cough or decreased level of
desaturation related to airway consciousness. Note: Suctioning can cause
secretions. increased hypoxemia; hyper oxygenate before,
during, and after suctioning.
Maintain adequate hydration by forcing Fluids, especially warm liquids, aid in
fluids to at least 3000 mL/day unless mobilization and expectoration of secretions.
contraindicated (e.g., heart failure). Fluids help maintain hydration and increases
Offer warm, rather than cold, fluids. ciliary action to remove secretions and reduces the
4