Page 119 - ANUAL REPORT MOH 2017
P. 119
HEALTH IMPACT ASSESSMENT OF AIR POLLUTION
In 2017, EHU focus on capacity building for estimation of disease burden due to air pollution. In
collaboration with WHO expert, EHU conducted a workshop on calculation of disease burden due
to air pollution using software Air Q+ produced by WHO. In total 25 participants from state health
department and local universities had attended the workshop. In collaboration with Thematic Working
Group on Air Quality of Regional Forum, EHU had estimated the disease burden due to air pollution
for four areas (Kuala Lumpur, Johor Bahru, Melaka Tengah, and Kuching). In addition, in 2017 EHU
had conducted the health risk assessment of particulate matter (PM10) exposure during haze among
adult population based on physical activity pattern. The aim of the health risk assessment was to
determine the acceptable duration for performing outdoor physical activity during haze as measured
by Air Pollutant Index (API) level.
DISEASE SURVEILLANCE SECTOR
• Influenza Surveillance Programme
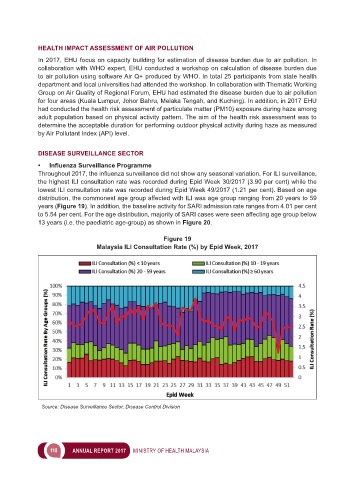
Throughout 2017, the influenza surveillance did not show any seasonal variation. For ILI surveillance,
the highest ILI consultation rate was recorded during Epid Week 30/2017 (3.90 per cent) while the
lowest ILI consultation rate was recorded during Epid Week 49/2017 (1.21 per cent). Based on age
distribution, the commonest age group affected with ILI was age group ranging from 20 years to 59
years (Figure 19). In addition, the baseline activity for SARI admission rate ranges from 4.01 per cent
to 5.54 per cent. For the age distribution, majority of SARI cases were seen affecting age group below
13 years (i.e. the paediatric age-group) as shown in Figure 20.
Figure 19
Malaysia ILI Consultation Rate (%) by Epid Week, 2017
Source: Disease Surveillance Sector, Disease Control Division
118 ANNUAL REPORT 2017 MINISTRY OF HEALTH MALAYSIA