Page 66 - Jolliffe I. Principal Component Analysis
P. 66
35
3.2. Geometric Properties of Sample Principal Components
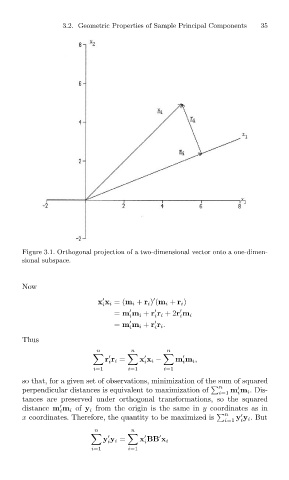
Figure 3.1. Orthogonal projection of a two-dimensional vector onto a one-dimen-
sional subspace.
Now
x x i =(m i + r i ) (m i + r i )
i
= m m i + r r i +2r m i
i i i
= m m i + r r i .
i i
Thus
n n n
r r i = x x i − m m i ,
i i i
i=1 i=1 i=1
so that, for a given set of observations, minimization of the sum of squared
perpendicular distances is equivalent to maximization of n m m i .Dis-
i=1 i
tances are preserved under orthogonal transformations, so the squared
distance m m i of y i from the origin is the same in y coordinates as in
i
x coordinates. Therefore, the quantity to be maximized is n y y i . But
i=1 i
n n
y y i =
i x BB x i
i
i=1 i=1