Page 302 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 302
GEOLOGY, GEOGRAPHY, AND METEOROLOGY
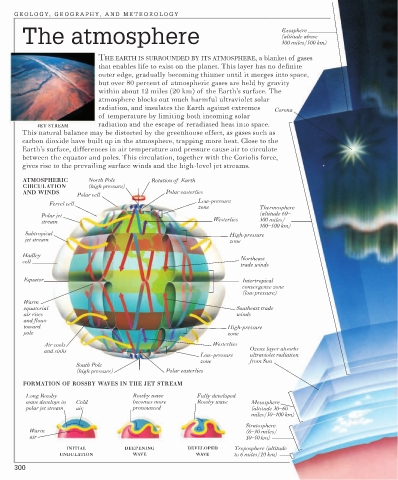
The atmosphere Exosphere
(altitude above
300 miles/500 km)
THE EARTH IS SURROUNDED BY ITS ATMOSPHERE, a blanket of gases
that enables life to exist on the planet. This layer has no definite
outer edge, gradually becoming thinner until it merges into space,
but over 80 percent of atmospheric gases are held by gravity
within about 12 miles (20 km) of the Earth’s surface. The
atmosphere blocks out much harmful ultraviolet solar
radiation, and insulates the Earth against extremes
Corona
of temperature by limiting both incoming solar
JET STREAM radiation and the escape of reradiated heat into space.
This natural balance may be distorted by the greenhouse effect, as gases such as
carbon dioxide have built up in the atmosphere, trapping more heat. Close to the
Earth’s surface, differences in air temperature and pressure cause air to circulate
between the equator and poles. This circulation, together with the Coriolis force,
gives rise to the prevailing surface winds and the high-level jet streams.
ATMOSPHERIC North Pole Rotation of Earth
CIRCULATION (high pressure)
AND WINDS Polar easterlies
Polar cell
Low-pressure
Ferrel cell
zone Thermosphere
Polar jet (altitude 60–
Westerlies 300 miles/
stream
100–500 km)
Subtropical High-pressure
jet stream zone
Hadley Northeast
cell
trade winds
Equator Intertropical
convergence zone
(low pressure)
Warm
equatorial Southeast trade
air rises winds
and flows
toward High-pressure
pole zone
Air cools Westerlies
and sinks Ozone layer absorbs
Low-pressure ultraviolet radiation
zone from Sun
South Pole
(high pressure) Polar easterlies
FORMATION OF ROSSBY WAVES IN THE JET STREAM
Long Rossby Rossby wave Fully developed
wave develops in Cold becomes more Rossby wave Mesosphere
polar jet stream air pronounced (altitude 30–60
miles/50–100 km)
Stratosphere
Warm (6–30 miles/
air 10–50 km)
INITIAL DEEPENING DEVELOPED Troposphere (altitude
UNDULATION WAVE WAVE to 6 miles/10 km)
300