Page 15 - (DK) Help Your Kids with Language Arts
P. 15
13
SPOKEN AND WRIT TEN LANGU AGE
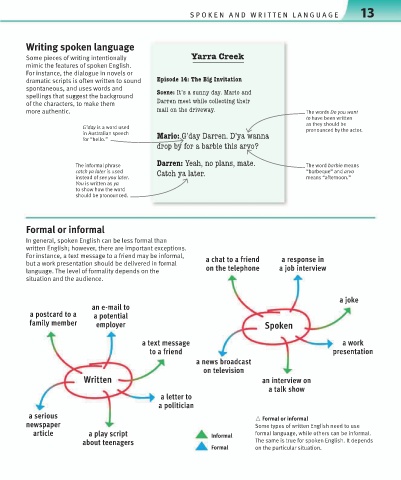
Writing spoken language
Some pieces of writing intentionally AIZZI +ZMMS
mimic the features of spoken English.
For instance, the dialogue in novels or
dramatic scripts is often written to sound -XQ[WLM " <PM *QO 1V^Q\I\QWV
spontaneous, and uses words and ;KMVM" 1\¼[ I []VVa LIa 5IZQW IVL
spellings that suggest the background
of the characters, to make them ,IZZMV UMM\ _PQTM KWTTMK\QVO \PMQZ
more authentic. UIQT WV \PM LZQ^M_Ia The words Do you want
to have been written
as they should be
G’day is a word used pronounced by the actor.
in Australian speech 5IZQW" /¼LIa ,IZZMV ,¼aI _IVVI
for “hello.”
LZWX Ja NWZ I JIZJQM \PQ[ IZ^W'
,IZZMV" AMIP VW XTIV[ UI\M
The informal phrase The word barbie means
catch ya later is used +I\KP aI TI\MZ “barbeque” and arvo
instead of see you later. means “afternoon.”
You is written as ya
to show how the word
should be pronounced.
Formal or informal
In general, spoken English can be less formal than
written English; however, there are important exceptions.
For instance, a text message to a friend may be informal, a chat to a friend a response in
but a work presentation should be delivered in formal
language. The level of formality depends on the on the telephone a job interview
situation and the audience.
a joke
an e-mail to
a postcard to a a potential
family member employer Spoken
a text message a work
to a friend presentation
a news broadcast
on television
Written an interview on
a talk show
a letter to
a politician
a serious △ Formal or informal
newspaper Some types of written English need to use
article a play script Informal formal language, while others can be informal.
about teenagers The same is true for spoken English. It depends
Formal on the particular situation.