Page 19 - Spotlight A+ SPM Additional Mathematics Form 4 & 5
P. 19
Form
4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Vectors
Paper 1
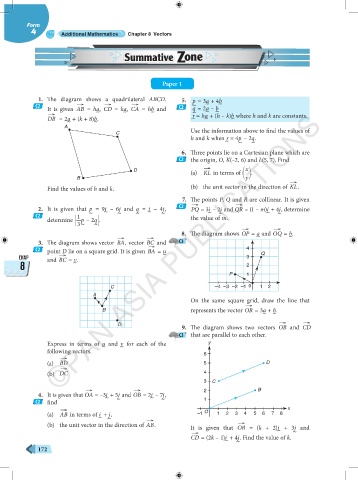
1. The diagram shows a quadrilateral ABCD. 5. p = 3a + 4b
→
→
→
C2 It is given AB = ha, CD = ka, CA = hb and C2 ∼ ∼ ∼
q = 2a – b
r = ha + (h – k)b where h and k are constants.
→ ∼ ∼ ∼ ∼ ∼ ∼
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
DB = 2a + (k + 8)b. ∼ ∼ ∼
∼
∼
A
C Use the information above to find the values of
h and k when r = 4p – 2q.
∼
∼
∼
6. Three points lie on a Cartesian plane which are
C2 the origin, O, K(–2, 6) and L(5, 7). Find
→ x
D (a) KL in terms of .
B y
→
Find the values of h and k. (b) the unit vector in the direction of KL.
7. The points P, Q and R are collinear. It is given
2. It is given that p = 9i – 6j and q = i – 4j, C2 → ∼ → ∼
PQ = 3i – 2j and QR = (1 – m)i + 4j, determine
∼
∼
∼
C2 1 ∼ ∼ ∼ ∼ the value of m. ∼
p – 2q .
determine 3 ∼ ∼
→ →
8. The diagram shows OP = a and OQ = b.
→ → ∼ ∼
3. The diagram shows vector BA, vector BC and C3
→
C2 point D lie on a square grid. It is given BA = u 4
→
CHAP and BC = v. ∼ 3 Q
8 ∼ 2
P 1
C –4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2
A
On the same square grid, draw the line that
→
B represents the vector OR = 3a + b.
∼
∼
→
→
D 9. The diagram shows two vectors OB and CD
C3 that are parallel to each other.
Express in terms of u and v for each of the y
∼
∼
following vectors. 6
→
(a) BD 5 D
→
(b) DC 4
3 C
→ → 2 B
4. It is given that OA = –3i + 5j and OB = 2i – 7j,
∼
∼
C2 find ∼ ∼ 1
→ x
(a) AB in terms of i + j, –1 O 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
∼
∼
→
(b) the unit vector in the direction of AB. It is given that OB = (k + 2)i + 3j and
→
→ ∼ ∼
CD = (2k – 1)i + 4j. Find the value of k.
∼
∼
172