Page 34 - Spotlight A+ Form 4 & 5 Mathematics KSSM
P. 34
Form
5
Chapter 8 Mathematical Modeling Mathematics
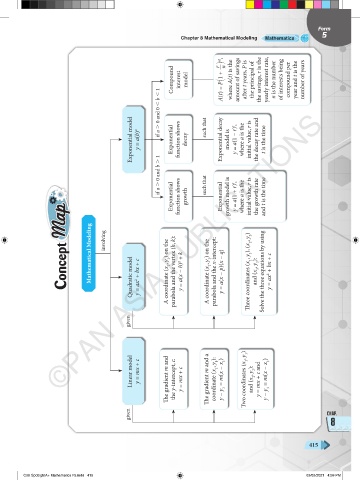
Compound interest model r A(t) = P 1 1 + —2 nt , n where A(t) is the amount of savings after t years, P is the principal of the savings, r is the yearly interest rate, n is the number of interests being compound per year and t is the number of years
if a . 0 and 0 , b , 1
Exponential model y = a(b) x Exponential function shows decay such that Exponential decay model is y = a(1 − r) t , where a is the initial value, r is the decay rate and t is the time
if a . 0 and b . 1 such that
Exponential function shows growth Exponential growth model is y = a(1 + r) t , where a is the initial value, r is the growth rate and t is the time
Mathematical Modeling
Solve the three equations by using
involving
Three coordinates (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 )
parabola and the vertex (h, k):
parabola and the x-intercept:
A coordinate (x 1 , y 1 ) on the
A coordinate (x 1 , y 1 ) on the
Concept ©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
y = a(x − p)(x − q)
y = a(x − h) 2 + k
y = ax 2 + bx + c
Quadratic model
and (x 3 , y 3 ):
y = ax 2 + bx + c
given
Linear model y = mx + c The gradient m and the y-intercept, c: y = mx + c The gradient m and a coordinate (x 1 , y 1 ): y − y 1 = m(x − x 1 ) Two coordinates (x 1 , y 1 ) and (x 2 , y 2 ): y = mx + c and y − y 1 = m(x − x 1 )
given CHAP.
8
PB 415
C08 SpotlightA+ Mathematics F5.indd 415 03/03/2021 4:59 PM