Page 1301 - (ISC)² CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study Guide
P. 1301
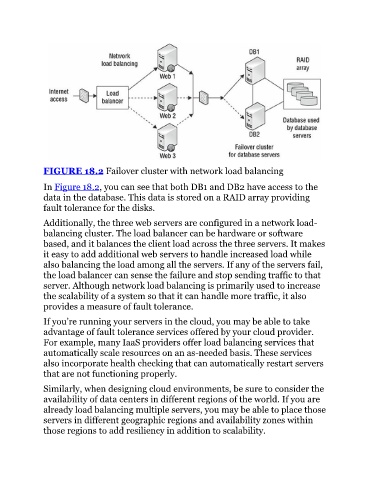
FIGURE 18.2 Failover cluster with network load balancing
In Figure 18.2, you can see that both DB1 and DB2 have access to the
data in the database. This data is stored on a RAID array providing
fault tolerance for the disks.
Additionally, the three web servers are configured in a network load-
balancing cluster. The load balancer can be hardware or software
based, and it balances the client load across the three servers. It makes
it easy to add additional web servers to handle increased load while
also balancing the load among all the servers. If any of the servers fail,
the load balancer can sense the failure and stop sending traffic to that
server. Although network load balancing is primarily used to increase
the scalability of a system so that it can handle more traffic, it also
provides a measure of fault tolerance.
If you’re running your servers in the cloud, you may be able to take
advantage of fault tolerance services offered by your cloud provider.
For example, many IaaS providers offer load balancing services that
automatically scale resources on an as-needed basis. These services
also incorporate health checking that can automatically restart servers
that are not functioning properly.
Similarly, when designing cloud environments, be sure to consider the
availability of data centers in different regions of the world. If you are
already load balancing multiple servers, you may be able to place those
servers in different geographic regions and availability zones within
those regions to add resiliency in addition to scalability.