Page 560 - (ISC)² CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study Guide
P. 560
configuration, installing device drivers, or modifying security settings.
Basically, any function not occurring in the user mode (ring 3) or
problem state takes place in the supervisory mode.
Stopped When a process finishes or must be terminated (because an
error occurs, a required resource is not available, or a resource request
can’t be met), it goes into a stopped state. At this point, the operating
system can recover all memory and other resources allocated to the
process and reuse them for other processes as needed.
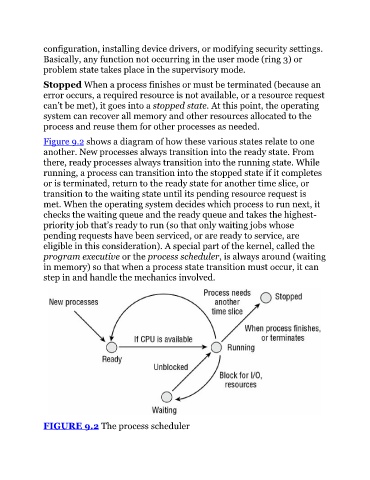
Figure 9.2 shows a diagram of how these various states relate to one
another. New processes always transition into the ready state. From
there, ready processes always transition into the running state. While
running, a process can transition into the stopped state if it completes
or is terminated, return to the ready state for another time slice, or
transition to the waiting state until its pending resource request is
met. When the operating system decides which process to run next, it
checks the waiting queue and the ready queue and takes the highest-
priority job that’s ready to run (so that only waiting jobs whose
pending requests have been serviced, or are ready to service, are
eligible in this consideration). A special part of the kernel, called the
program executive or the process scheduler, is always around (waiting
in memory) so that when a process state transition must occur, it can
step in and handle the mechanics involved.
FIGURE 9.2 The process scheduler