Page 830 - (ISC)² CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study Guide
P. 830
data. If the data is not addressed to a specific system, that system just
ignores the data. The benefit of a bus topology is that if a single
segment fails, communications on all other segments continue
uninterrupted. However, the central trunk line remains a single point
of failure.
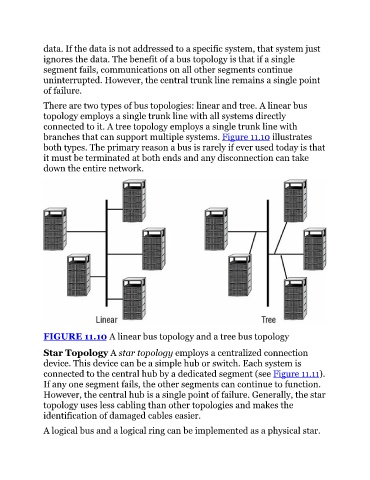
There are two types of bus topologies: linear and tree. A linear bus
topology employs a single trunk line with all systems directly
connected to it. A tree topology employs a single trunk line with
branches that can support multiple systems. Figure 11.10 illustrates
both types. The primary reason a bus is rarely if ever used today is that
it must be terminated at both ends and any disconnection can take
down the entire network.
FIGURE 11.10 A linear bus topology and a tree bus topology
Star Topology A star topology employs a centralized connection
device. This device can be a simple hub or switch. Each system is
connected to the central hub by a dedicated segment (see Figure 11.11).
If any one segment fails, the other segments can continue to function.
However, the central hub is a single point of failure. Generally, the star
topology uses less cabling than other topologies and makes the
identification of damaged cables easier.
A logical bus and a logical ring can be implemented as a physical star.