Page 920 - (ISC)² CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study Guide
P. 920
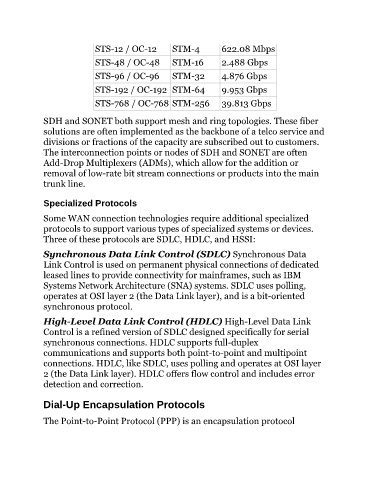
STS-12 / OC-12 STM-4 622.08 Mbps
STS-48 / OC-48 STM-16 2.488 Gbps
STS-96 / OC-96 STM-32 4.876 Gbps
STS-192 / OC-192 STM-64 9.953 Gbps
STS-768 / OC-768 STM-256 39.813 Gbps
SDH and SONET both support mesh and ring topologies. These fiber
solutions are often implemented as the backbone of a telco service and
divisions or fractions of the capacity are subscribed out to customers.
The interconnection points or nodes of SDH and SONET are often
Add-Drop Multiplexers (ADMs), which allow for the addition or
removal of low-rate bit stream connections or products into the main
trunk line.
Specialized Protocols
Some WAN connection technologies require additional specialized
protocols to support various types of specialized systems or devices.
Three of these protocols are SDLC, HDLC, and HSSI:
Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC) Synchronous Data
Link Control is used on permanent physical connections of dedicated
leased lines to provide connectivity for mainframes, such as IBM
Systems Network Architecture (SNA) systems. SDLC uses polling,
operates at OSI layer 2 (the Data Link layer), and is a bit-oriented
synchronous protocol.
High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) High-Level Data Link
Control is a refined version of SDLC designed specifically for serial
synchronous connections. HDLC supports full-duplex
communications and supports both point-to-point and multipoint
connections. HDLC, like SDLC, uses polling and operates at OSI layer
2 (the Data Link layer). HDLC offers flow control and includes error
detection and correction.
Dial-Up Encapsulation Protocols
The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is an encapsulation protocol