Page 349 - Math Smart - 7
P. 349
CHAPTER 15.3
In this chapter
Pupils should be able to:
Volume of Cubes and • derive and use the
formula for the volume
Cuboids • of a cuboid
calculate volumes of
cuboids
In Stages 3 and 5, you learnt about cuboids and cubes. Let us recall some
properties of these solids. A 2D shape has two dimensions — length and width.
A solid is a 3D object with three dimensions — length, width and height.
Think and
What is a cube? What is a cuboid? What are some similarities and differences
between a cube and a cuboid?
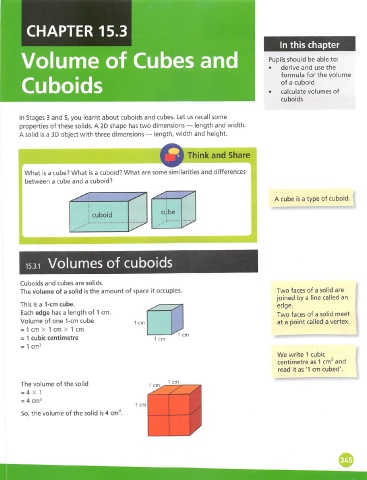
A cube is a type of cuboid.
cube
: cuboid
Volumes of cuboids
Cuboids and cubes are solids.
The volume of a solid is the amount of space it occupies. Two faces of a solid are
joined by a line called an
This is a 1-cm cube. edge.
Each edge has a length of 1 cm. Two faces of a solid meet
Volume of one 1-cm cube 1 crn at a point called a vertex.
= 1 cm X 1 cm X 1 cm
1 cm
= 1 cubic centimetre 1 cm
= 1 cm^
We write 1 cubic
centimetre as 1 cm^ and
read it as '1 cm cubed'.
1 cm
The volume of the solid
= 4 X 1
= 4 cm^ . I:
1 cm
So, the volume of the solid is 4 cm^.
r