Page 51 - Elementary_Linear_Algebra_with_Applications_Anton__9_edition
P. 51
and column j of is the entry in row j and column i of A; that is,
(11)
Note the reversal of the subscripts.
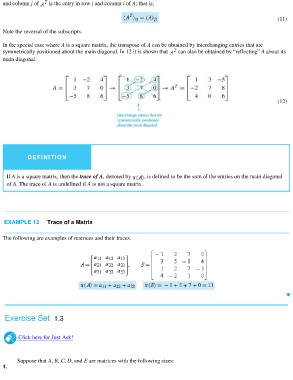
In the special case where A is a square matrix, the transpose of A can be obtained by interchanging entries that are
symmetrically positioned about the main diagonal. In 12 it is shown that can also be obtained by “reflecting” A about its
main diagonal.
(12)
DEFINITION
If A is a square matrix, then the trace of A, denoted by , is defined to be the sum of the entries on the main diagonal
of A. The trace of A is undefined if A is not a square matrix.
EXAMPLE 12 Trace of a Matrix
The following are examples of matrices and their traces.
Exercise Set 1.3
Click here for Just Ask!
Suppose that A, B, C, D, and E are matrices with the following sizes:
1.