Page 183 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 183
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts] 1. Mathematics for Structural mechanics
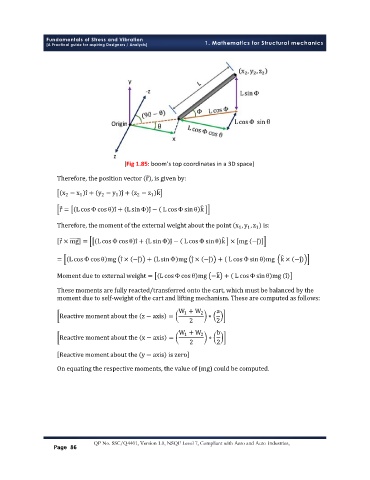
[Fig 1.85: boom’s top coordinates in a 3D space]
Therefore, the position vector r , is given by:
x − x i + y − y j + z − z k
1
2
1
1
2
2
r = L cos Φ cos θ i + L sinΦ j − L cosΦ sinθ k
Therefore, the moment of the external weight about the point x , y , z is:
1
1
1
r × mg = L cos Φ cos θ i + L sinΦ j − L cosΦ sin θ k × mg −j
= L cos Φ cos θ mg i × −j + L sin Φ mg j × −j + L cos Φ sin θ mg k × −j
Moment due to external weight = L cos Φ cos θ mg −k + L cosΦ sinθ mg i
These moments are fully reacted/transferred onto the cart, which must be balanced by the
moment due to self-weight of the cart and lifting mechanism. These are computed as follows:
W + W a
Reactive moment about the z − axis = 1 2 ∗
2 2
b
Reactive moment about the x − axis = W + W 2 ∗
1
2 2
Reactive moment about the y − axis is zero
On equating the respective moments, the value of (mg) could be computed.
QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries,
Page 86