Page 307 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 307
Role of Nerve Conduction Study 283
in Diabetic Patients
• Small-fiber neuropathy Treatment related Neuropathy of ketoaci-
• Autonomic neuropathy dosis
Neuropathy of chronic
• Large-fiber sensory neuropathy renal failure
Neuropathy associated
Focal and Asymmetrical Neuropathies with large vessel ischemia
Insulin neuritis Hyperinsu-
• Cranial neuropathy (single or multiple) lin neuropathy
• Truncal neuropathy (thoracic radiculopathy)
Features of Diabetic Neuropathy
• Limb mononeuropathy (single or multiple)
• Common complication affecting up to 50% pa-
• Proximal motor neuropathy (lumbosacral radiculo- tients with Diabetes mellitus.
plexopathy, amyotrophy)
• Frequently asymptomatic
• Requires careful examination/assessment to de-
tect .
• The dermatological assessment should initially
include a global inspection,(interdigitally also), for
the presence of ulceration or areas of abnormal
erythema. The presence of callus (particularly with
haemorrhage), nail dystrophy, ingrown toe nail or
paronychia should be recorded, Focal or global
skin temperature differences between one foot
and the other may be predictive of either vascular
disease or Cellulitis associated with or without ul-
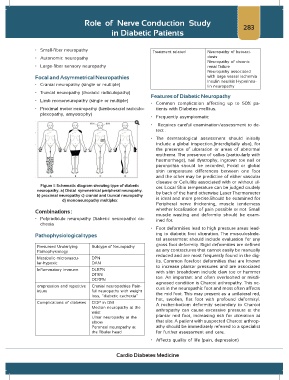
Figure 1: Schematic diagram showing type of diabetic cer. Local Skin temperature can be judged crudely
neuropathy. a) Distal symmetrical peripheral neuropahy. by back of the hand otherwise Laser Thermometer
b) proximal neuropathy c) cranial and truncal neuropathy
d) mononeuropathy multiplex is ideal and more precise.Should be examined for
Peripheral nerve thickening, muscle tenderness
Combinations : whether localization of pain possible or not. Small
muscle wasting and deformity should be exam-
• Polyradiculo neuropathy Diabetic neuropathic ca- ined for.
chexia
• Foot deformities lead to high pressure areas lead-
Pathophysiological types ing to diabetic foot ulceration. The musculoskele-
tal assessment should include evaluation for any
gross foot deformity. Rigid deformities are defined
Presumed Underlying Subtype of Neuropathy
Pathophysiology as any contractures that cannot easily be manually
reduced and are most frequently found in the dig-
Metabolic-microvascu- DPN
lar-hypoxic DAN its. Common forefoot deformities that are known
to increase plantar pressures and are associated
Inflammatory immune DLRPN with skin breakdown include claw toe or hammer
DTRN
DCRPN toe. An important and often overlooked or misdi-
agnosed condition is Charcot arthropathy. This oc-
ompression and repetitive Cranial neuropathies Pain- curs in the neuropathic foot and most often affects
injury ful neuropathy with weight the mid foot. This may present as a unilateral red,
loss, “diabetic cachexia”
hot, swollen, flat foot with profound deformity1.
Complications of diabetes CIDP in DM A rocker-bottom deformity secondary to Charcot
Median neuropathy at the arthropathy can cause excessive pressure at the
wrist
Ulnar neuropathy at the plantar mid foot, increasing risk for ulceration at
elbow that site. A patient with suspected Charcot arthrop-
Peroneal neuropathy at athy should be immediately referred to a specialist
the fibular head for further assessment and care.
• Affects quality of life (pain, depression)
Cardio Diabetes Medicine