Page 344 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 344
320 Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017
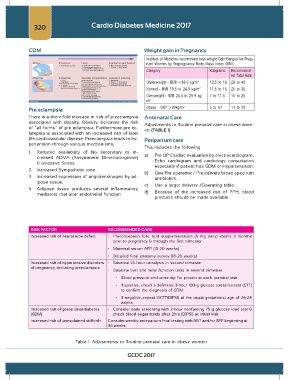
GDM Weight gain in Pregnancy
Institute of Medicine recommend total weight Gain Ranges for Preg-
nant Women by Prepregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI)
Category Kilograms Recommend-
ed Total Gain
Underweight - BMI <18.5 kg/m 2 12.5 to 18 28 to 40
Normal - BMI 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m 2 11.5 to 16 25 to 35
Overweight - BMI 25.5 to 29.9 kg/ 7 to 11.5 15 to 25
m 2
Pre eclampsia Obese - BMI >30kg/m 2 5 to 9.1 11 to 20
There is a there fold increase in risk of preeclampsia Antenatal Care
associated with obesity. Obesity increases the risk Adjustments to Routine prenatal care in obese wom-
of “all forms” of pre eclampsia. Furthermore pre ec- en (TABLE 1)
lampsia is associated with an increased risk of later
life cardiovascular disease. Preeclampsia leads to hy- Peripartum care
pertension through various mechanisms,
This includes the following
1. Reduced availability of No secondary to in-
creased ADMA (Assymmetic Dimethylarginine) a) Pre OP Cardiac evaluation by electrocardiogram,
& oxidative Stress. Echo cardiogram and cardiology consultation
especially if patient has GDM or Hypertensiuon.
2. Increased Sympathetic tone. b) Give Pre operative / Pre delivery broad spectrum
3. Increased expression of angiotensinogen by ad- antibiotics.
ipose tissue.
c) Use a larger delivery /Operating table.
4. Adipose tissue produces several inflammatory
mediators that alter endothelial function d) Because of the increased risk of PPH, blood
products should be made available.
RISK FACTOR RECOMMENDED CARE
Increased risk of neural tube defect • Preconception folic acid supplementation (4 mg daily) ideally 3 months
prior to pregnancy & through the first trimester
• Maternal serum AFP (15-20 weeks)
• Detailed fetal anatomy survey (18-20 weeks)
Increased risk of hypertensive disorders • Baseline 24-hour urinalysis in second trimester
of pregnancy, including preeclampsia
• Baseline liver and renal function tests in second trimester
• Blood pressure and urine dip for protein at each prenatal visit
• If positive, check a definitive 3-hour 100-g glucose tolerance test (GTT)
to confirm the diagnosis of GDM
• If negative, repeat OGTT(DIPSI) at the usual gestational age of 24-28
weeks
Increased risk of gestational diabetes • Consider early screening with 2-hour nonfasting 75-g glucose load test &
(GDM) check blood sugar levels after 2hrs (DIPSI) at initial visit
Increased risk of unexplained stillbirth Consider weekly antepartum fetal testing with NST and/or BPP beginning at
36 weeks
Table 1: Adjustments to Routine prenatal care in obese women
GCDC 2017