Page 339 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 339
Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017 315
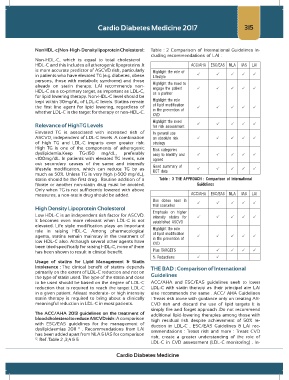
Non HDL-c (Non-High-Density lipoprotein Cholesterol: Table : 2 Comparison of International Guidelines In-
cluding recommendations of LAI :
Non-HDL-C, which is equal to total cholesterol –
HDL-C and this includes all atherogenic lipoproteins .It ACC/AHA ESC/EAS NLA IAS LAI
is more accurate predictor of ASCVD risk, particularly Highlight the role of
in patients who have elevated TG (e.g. diabetes, obese Lifestyle
persons, those with metabolic syndrome) and those
already on statin therapy. LAI recommends non- Highlight the need to
engage the patient
HDL-C as a co-primary target, as important as LDL-C, as a partner
for lipid lowering therapy. Non-HDL-C level should be
kept within 30mg/dL of LDL-C levels. Statins remain Highlight the role
the first line agent for lipid lowering, regardless of of lipid modification
whether LDL-C is the target for therapy or non-HDL-C. in the prevention of
CVD
Highlight the need
Relevance of HighTG Levels for risk assessment
Elevated TG is associated with increased risk of In general use
ASCVD, independent of LDL-C levels. A combination an absolute risk
of high TG and LDL-C imparts even greater risk. strategy
High TG is one of the components of atherogenic Risk categories
dyslipidemia.Keep TG<150 mg/dL, preferably easy to identify and
<100mg/dL. In patients with elevated TG levels, rule agreed
out secondary causes of the same and intensify Good summary of
lifestyle modification, which can reduce TG by as RCT data
much as 50%. Unless TG is very high (>500 mg/dL),
statin should be the first drug . Routine addition of a Table : 3 THE APPROACH : Comparison of International
fibrate or another non-statin drug must be avoided. Guidelines
Only when TG is not sufficiently lowered with above
measures, a non-statin drug should be added. ACC/AHA ESC/EAS NLA IAS LAI
Use doses seen in
trial scenarios
High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol
Emphasis on higher
Low HDL-C is an independent risk factor for ASCVD. intensity statins for
It becomes even more relevant when LDL-C is not established ASCVD
elevated. Life style modification plays an important
role in raising HDL-C. Among pharmacological Highlight the role
of lipid modification
agents, statins remain mainstay in the treatment of in the prevention of
low HDL-C also. Although several other agents have CVD
been tried specifically for raising HDL-C, none of them
has been shown to result in clinical benefit. Plus TARGETS
% Reductions √
Usage of statins for Lipid Management & Statin
Intolerance : The clinical benefit of statins depends THE BAD : Comparison of International
primarily on the extent of LDL-C reduction and not on
the type of statin used. The type of the statin and dose Guidelines
to be used should be based on the degree of LDL-C ACC/AHA and ESC/EAS guidelines seek to lower
reduction that is required to reach the target LDL-C LDL-C with statin therapy as their principal aim LAI
in a given patient. Atleast moderate- or high intensity also recommends the same . ACC/ AHA Guidelines
statin therapy is required to bring about a clinically : Treats risk alone with guidance only on treating AS-
meaningful reduction in LDL-C in most patients. CVD risk and discard the use of lipid targets It is
simply fire and forget approach .Do not recommend
The ACC/AHA 2013 guidelines on the treatment of additional lipid-lowering therapies among those with
blood cholesterol to reduce ASCVD risk : A comparison high residual risk despite achievement of 50% re-
with ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of duction in LDL-C . ESC/EAS Guidelines & LAI rec-
11
dyslipidaemias 2011 . Recommendations from LAI ommendations : Treats risk and more : Treats CVD
has been added apart from NLA & IAS for comparison
12 . Ref .Table 2 ,3,4 & 5 risk, create a greater understanding of the role of
LDL-C in CVD assessment (LDL-C monitoring) . In-
Cardio Diabetes Medicine