Page 128 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 128
Determining the e.m.f. and Internal Resistance of a Dry Cell
x t 3.5
Aim: To determine the e.m.f. and internal resistance of a dry cell
Apparatus: 1.5 V dry cell, cell holder, switch, connecting wires, ammeter, voltmeter and rheostat
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
Procedure:
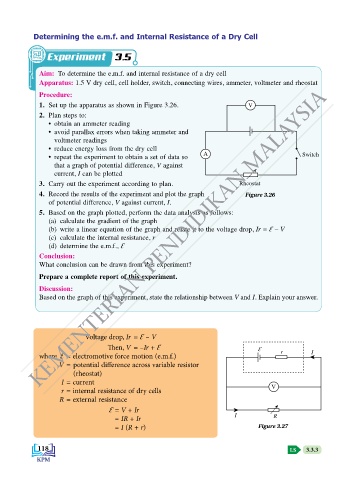
1. Set up the apparatus as shown in Figure 3.26. V
2. Plan steps to:
• obtain an ammeter reading
• avoid parallax errors when taking ammeter and
voltmeter readings
• reduce energy loss from the dry cell
A Switch
• repeat the experiment to obtain a set of data so
that a graph of potential difference, V against
current, I can be plotted
3. Carry out the experiment according to plan. Rheostat
4. Record the results of the experiment and plot the graph Figure 3.26
of potential difference, V against current, I.
5. Based on the graph plotted, perform the data analysis as follows:
(a) calculate the gradient of the graph
(b) write a linear equation of the graph and relate it to the voltage drop, Ir = Ԑ – V
(c) calculate the internal resistance, r
(d) determine the e.m.f., Ԑ
Conclusion:
What conclusion can be drawn from this experiment?
Prepare a complete report of this experiment.
Discussion:
Based on the graph of this experiment, state the relationship between V and I. Explain your answer.
Voltage drop, Ir = Ԑ – V
Then, V = –Ir + Ԑ Ԑ
where Ԑ = electromotive force motion (e.m.f.) r I
V = potential difference across variable resistor
(rheostat)
I = current
r = internal resistance of dry cells V
R = external resistance
Ԑ = V + Ir
= IR + Ir I R
= I (R + r) Figure 3.27
118 LS 3.3.3