Page 167 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 167
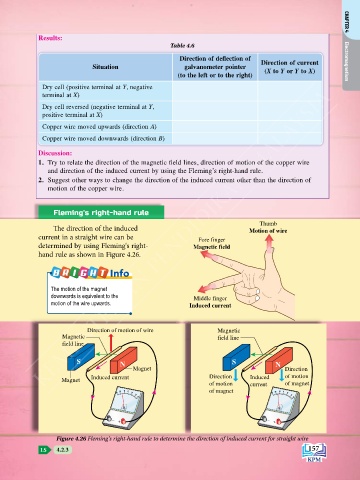
Results: CHAPTER 4
Table 4.6
Direction of deflection of
Direction of current Electromagnetism
Situation galvanometer pointer (X to Y or Y to X)
(to the left or to the right)
Dry cell (positive terminal at Y, negative
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
terminal at X)
Dry cell reversed (negative terminal at Y,
positive terminal at X)
Copper wire moved upwards (direction A)
Copper wire moved downwards (direction B)
Discussion:
1. Try to relate the direction of the magnetic field lines, direction of motion of the copper wire
and direction of the induced current by using the Fleming’s right-hand rule.
2. Suggest other ways to change the direction of the induced current other than the direction of
motion of the copper wire.
Fleming's right-hand rule
Thumb
The direction of the induced Motion of wire
current in a straight wire can be Fore finger
determined by using Fleming's right- Magnetic field
hand rule as shown in Figure 4.26.
Info
The motion of the magnet
downwards is equivalent to the Middle finger
motion of the wire upwards. Induced current
Direction of motion of wire Magnetic
Magnetic field line
field line
S N S N
Magnet Direction
Induced current Direction Induced of motion
Magnet
of motion current of magnet
20 10 0 of magnet 20 10 0
30 10 20 30 30 10 20 30
– –
+ +
Figure 4.26 Fleming's right-hand rule to determine the direction of induced current for straight wire
LS 4.2.3 157