Page 190 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 190
Chapter 4 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL CARDIAC RHY THM DISTURBANCE NEEDS 175
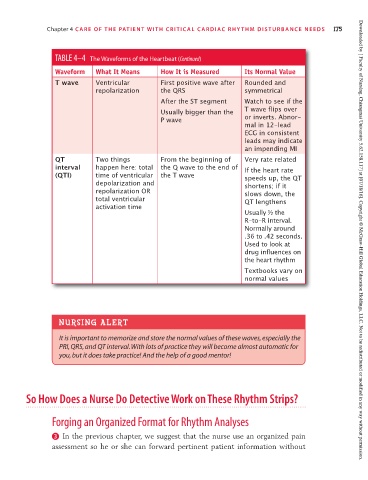
TABLE 4–4 The Waveforms of the Heartbeat (Continued)
Waveform What It Means How It is Measured Its Normal Value
T wave Ventricular First positive wave after Rounded and
repolarization the QRS symmetrical
After the ST segment Watch to see if the
Usually bigger than the T wave flips over
P wave or inverts. Abnor-
mal in 12-lead
ECG in consistent
leads may indicate
an impending MI
QT Two things From the beginning of Very rate related
interval happen here: total the Q wave to the end of If the heart rate
(QTI) time of ventricular the T wave speeds up, the QT
depolarization and shortens; if it
repolarization OR slows down, the
total ventricular QT lengthens
activation time
Usually ½ the
R-to-R interval.
Normally around
.36 to .42 seconds.
Used to look at Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
drug influences on
the heart rhythm
Textbooks vary on
normal values
NURSING ALERT
It is important to memorize and store the normal values of these waves, especially the
PRI, QRS, and QT interval. With lots of practice they will become almost automatic for
you, but it does take practice! And the help of a good mentor!
So How Does a Nurse Do Detective Work on These Rhythm Strips?
Forging an Organized Format for Rhythm Analyses
3 In the previous chapter, we suggest that the nurse use an organized pain
assessment so he or she can forward pertinent patient information without