Page 255 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 255
240 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
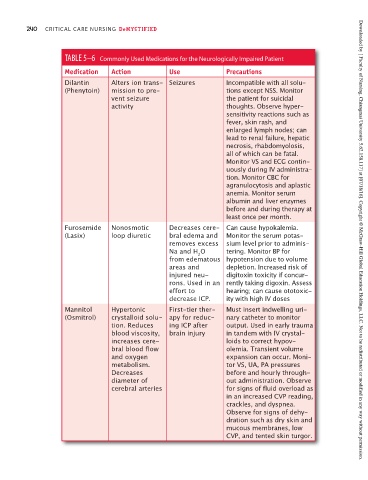
TABLE 5–6 Commonly Used Medications for the Neurologically Impaired Patient
Medication Action Use Precautions
Dilantin Alters ion trans- Seizures Incompatible with all solu-
(Phenytoin) mission to pre- tions except NSS. Monitor
vent seizure the patient for suicidal
activity thoughts. Observe hyper-
sensitivity reactions such as
fever, skin rash, and
enlarged lymph nodes; can
lead to renal failure, hepatic
necrosis, rhabdomyolosis,
all of which can be fatal.
Monitor VS and ECG contin-
uously during IV administra-
tion. Monitor CBC for
agranulocytosis and aplastic
anemia. Monitor serum
albumin and liver enzymes
before and during therapy at
least once per month.
Furosemide Nonosmotic Decreases cere- Can cause hypokalemia.
(Lasix) loop diuretic bral edema and Monitor the serum potas-
removes excess sium level prior to adminis- Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Na and H O tering. Monitor BP for
2
from edematous hypotension due to volume
areas and depletion. Increased risk of
injured neu- digitoxin toxicity if concur-
rons. Used in an rently taking digoxin. Assess
effort to hearing; can cause ototoxic-
decrease ICP. ity with high IV doses
Mannitol Hypertonic First-tier ther- Must insert indwelling uri-
(Osmitrol) crystalloid solu- apy for reduc- nary catheter to monitor
tion. Reduces ing ICP after output. Used in early trauma
blood viscosity, brain injury in tandem with IV crystal-
increases cere- loids to correct hypov-
bral blood flow olemia. Transient volume
and oxygen expansion can occur. Moni-
metabolism. tor VS, UA, PA pressures
Decreases before and hourly through-
diameter of out administration. Observe
cerebral arteries for signs of fluid overload as
in an increased CVP reading,
crackles, and dyspnea.
Observe for signs of dehy-
dration such as dry skin and
mucous membranes, low
CVP, and tented skin turgor.