Page 264 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 264
Chapter 5 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH NEUROLOGICAL NEEDS 249
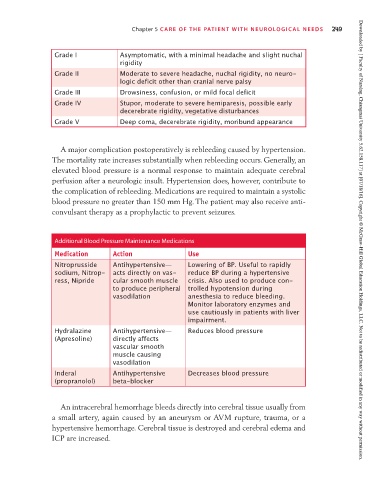
Grade I Asymptomatic, with a minimal headache and slight nuchal
rigidity
Grade II Moderate to severe headache, nuchal rigidity, no neuro-
logic deficit other than cranial nerve palsy
Grade III Drowsiness, confusion, or mild focal deficit
Grade IV Stupor, moderate to severe hemiparesis, possible early
decerebrate rigidity, vegetative disturbances
Grade V Deep coma, decerebrate rigidity, moribund appearance
A major complication postoperatively is rebleeding caused by hypertension.
The mortality rate increases substantially when rebleeding occurs. Generally, an
elevated blood pressure is a normal response to maintain adequate cerebral
perfusion after a neurologic insult. Hypertension does, however, contribute to
the complication of rebleeding. Medications are required to maintain a systolic
blood pressure no greater than 150 mm Hg. The patient may also receive anti-
convulsant therapy as a prophylactic to prevent seizures.
Additional Blood Pressure Maintenance Medications Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Medication Action Use
Nitroprusside Antihypertensive— Lowering of BP. Useful to rapidly
sodium, Nitrop- acts directly on vas- reduce BP during a hypertensive
ress, Nipride cular smooth muscle crisis. Also used to produce con-
to produce peripheral trolled hypotension during
vasodilation anesthesia to reduce bleeding.
Monitor laboratory enzymes and
use cautiously in patients with liver
impairment.
Hydralazine Antihypertensive— Reduces blood pressure
(Apresoline) directly affects
vascular smooth
muscle causing
vasodilation
Inderal Antihypertensive Decreases blood pressure
(propranolol) beta-blocker
An intracerebral hemorrhage bleeds directly into cerebral tissue usually from
a small artery, again caused by an aneurysm or AVM rupture, trauma, or a
hypertensive hemorrhage. Cerebral tissue is destroyed and cerebral edema and
ICP are increased.