Page 36 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 36
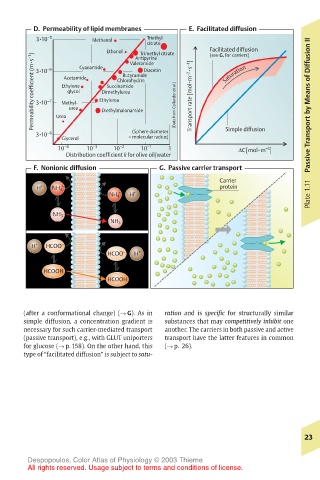
D. Permeability of lipid membranes E. Facilitated diffusion
3 •10 –5 Methanol Triethyl
citrate
Ethanol Valeramide Facilitated diffusion
Trimethyl citrate
(see G. for carriers)
Permeability coefficient (m •s –1 ) 3 •10 –7 Ethylene Ethylurea Chlorohydrin (Data from Collander et al.) Transport rate [mol •m –2 •s –1 ] Saturation Passive Transport by Means of Diffusion II
Antipyrine
Cyanamide
–6
Diacetin
3•10
Butyramide
Acetamide
Succinamide
glycol
Dimethylurea
Methyl-
urea
Diethylmalonamide
(Sphere diameter
3 •10 –8 Urea = molecular radius) Simple diffusion
Glycerol
10 –4 10 –3 10 –2 10 –1 1 ∆C[mol •m ]
–3
Distribution coefficient k for olive oil/water
F. Nonionic diffusion G. Passive carrier transport
Carrier
H + + NH 4 + protein
+
NH 4 + H + Plate 1.11
NH 3
NH 3
+
H + HCOO –
–
HCOO + H +
HCOOH
HCOOH
(after a conformational change) (! G). As in ration and is specific for structurally similar
simple diffusion, a concentration gradient is substances that may competitively inhibit one
necessary for such carrier-mediated transport another. The carriers in both passive and active
(passive transport), e.g., with GLUT uniporters transport have the latter features in common
for glucose (! p. 158). On the other hand, this (! p. 26).
type of “facilitated diffusion” is subject to satu-
23
23
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.