Page 58 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 58
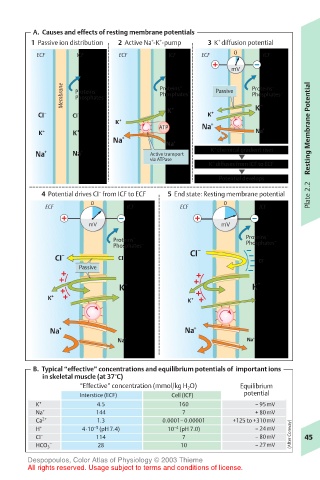
A. Causes and effects of resting membrane potentials
+
+
+
1 Passive ion distribution 2 Active Na -K -pump 3 K diffusion potential
ECF ICF ECF ICF ECF 0 ICF
mV
Membrane Proteins – – Proteins – – Passive Proteins – –
Phosphates
Phosphates
Phosphates
CI – CI – K + K + K +
K + +
ATP Na + Resting Membrane Potential
K + K + Na
Na +
Na + +
Na + Na + Active transport K chemical gradient rises
via ATPase
K diffuses from ICF to ECF
+
Potential develops
–
4 Potential drives CI from ICF to ECF 5 End state: Resting membrane potential Plate 2.2
0 0
ECF ICF ECF ICF
mV mV
Proteins – Proteins – –
Phosphates – – Phosphates
CI – CI – CI CI –
Passive
K + K +
K + K +
Na + Na +
Na + Na +
B. Typical “effective” concentrations and equilibrium potentials of important ions
in skeletal muscle (at 37°C)
“Effective” concentration (mmol/kg H 2 O) Equilibrium
Interstice (ECF) Cell (ICF) potential
K + 4.5 160 – 95mV
Na + 144 7 + 80mV
Ca 2+ 1.3 0.0001–0.00001 +125 to +310mV
–4
–5
H + 4·10 (pH 7.4) 10 (pH 7.0) – 24mV
CI – 114 7 – 80mV (After Conway) 45
– – 27mV
HCO 3 28 10
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.