Page 889 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 889
620 PART 5: Infectious Disorders
self-contained hospital nursing units outfitted with high-efficiency
particulate air filtration (HEPA) has reduced the incidence of invasive
aspergillosis and overall mortality rates. Guidelines are available for
426
427
planning infection control strategies where hospital maintenance and
renovation projects are underway. 428-430 HEPA-filtered nursing units have
lower concentrations of airborne fungal conidia than their non-HEPA-
filtered counterparts. Despite these observations, a meta-analysis of
431
the impact of HEPA-filtered protected environments failed to detect a
mortality benefit in neutropenic or nonneutropenic patients. A recent
432
systematic review did observe a treatment effect for preventing the
development of “all-cause” pulmonary infiltrates. 433
Invasive aspergillosis has high mortality rates regardless of treatment.
434
The risk of this infection increases with the duration of neutropenia to
a plateau of 70% to 80% at 5 weeks particularly in environments with
435
high degrees of contamination with mold conidia. Marrow recovery is
436
the most important factor relating to survival. 437
The clinical findings relate to the infected organ site. Fever is almost
invariably present. Evidence of tissue ischemia and infarction may pro-
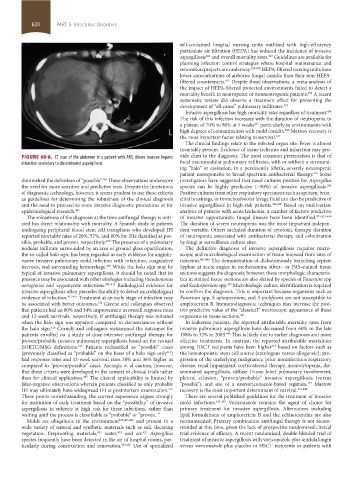
FIGURE 68-8. CT scan of the abdomen in a patient with AML shows massive hepatic vide clues to the diagnosis. The most common presentation is that of
infarction secondary to disseminated aspergillosis. focal macronodular pulmonary infiltrates, with or without a surround-
ing “halo” or cavitation, in a persistently febrile, severely neutropenic
patient unresponsive to broad-spectrum antibacterial therapy. Some
416
diminished the definition of “possible”. These observations underscore investigators have suggested that nasal cultures positive for Aspergillus
406
the need for more sensitive and predictive tests. Despite the limitations species can be highly predictive (~90%) of invasive aspergillosis.
286
of diagnostic technology, however, it seems prudent to use these criteria Positive cultures from other respiratory specimens such as sputum, bron-
as guidelines for determining the robustness of the clinical diagnosis chial brushings, or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid can also be predictive of
and the need to proceed to more invasive diagnostic procedures or for invasive aspergillosis in high-risk patients. 346,406 Based on multivariate
epidemiological research. 407 analysis of patients with acute leukemia, a number of factors predictive
The robustness of the diagnosis at the time antifungal therapy is initi- of invasive opportunistic fungal disease have been identified. 435,437-440
ated has direct relationship with mortality. A Spanish study in patients The duration of severe neutropenia was the most important indepen-
undergoing peripheral blood stem cell transplants who developed IFI dent variable. Others included duration of cytotoxic therapy, duration
reported mortality rates of 20%, 57%, and 80% for IFIs classified as pos- of neutropenia associated with antibacterial therapy, and colonization
sible, probable, and proven, respectively. The presence of a pulmonary by fungi at surveillance culture sites.
408
nodular infiltrate surrounded by an area of ground glass opacification, The definitive diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis requires micro-
the so-called halo sign, has been regarded as early evidence for angioin- scopic and microbiological examination of tissue biopsied from sites of
vasive invasive pulmonary mold infection with infarction, coagulative infection. 403,406 The demonstration of dichotomously branching septate
necrosis, and surrounding hemorrhage. While the halo sign may be hyphae at acute angles in methenamine silver– or PAS-stained tissue
409
typical of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, it should be noted that its sections suggests the diagnosis; however, these morphologic characteris-
presence may be associated with other etiologies including Pseudomonas tics in stained tissue sections are also shared by species of Fusarium spp
aeruginosa and zygomycete infections. 409-412 Radiological evidence for and Scedosporium spp. Microbiologic culture identification is required
403
invasive aspergillosis often precedes the ability to detect microbiological to confirm the diagnosis. This is important because organisms such as
evidence of infection. 413-415 Treatment at an early stage of infection may Fusarium spp, S apiospermum, and S prolificans are not susceptible to
be associated with better outcomes. Greene and colleagues observed amphotericin B. Immunodiagnostic techniques may increase the posi-
134
that patients had an 80% and 34% improvement in overall response rates tive predictive value of the “classical” microscopic appearance of these
and 12-week survivals, respectively, if antifungal therapy was initiated organisms in tissue sections. 441
when the halo sign was apparent compared to circumstances without In leukemia patients, the reported attributable mortality rates from
the halo sign. Cornely and colleagues reexamined the outcomes for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis have decreased from 60% in the late
416
patients enrolled on a study of dose-intensive antifungal therapy for 1980s to 32% in 2003. This is likely due to earlier diagnoses and more
442
proven/probable invasive pulmonary aspergillosis based on the revised effective treatments. In contrast, the reported attributable mortalities
EORTC/MSG definitions. Patients reclassified as “possible” cases among HSCT recipients have been higher based on factors such as
417
443
(previously classified as “probable” on the basis of a halo sign only ) the hematopoietic stem cell source (autologous versus allogeneic), pro-
418
had response rates and 12-week survival rates 28% and 36% higher as gression of the underlying malignancy, prior noninfectious respiratory
compared to “proven/possible” cases. Ascioglu et al caution, however, disease, renal impairment, corticosteroid therapy, monocytopenia, dis-
that these criteria were developed in the context of clinical trials rather seminated aspergillosis, diffuse (>one lobe) pulmonary involvement,
than for clinical application. The clinical applicability is limited by pleural effusion, “proven/probable” invasive aspergillosis (versus
405
false-negative observations wherein patients classified as only probable “possible”), and use of a nonvoriconazole-based regimen. Marrow
444
IFI may ultimately have widespread IFI at postmortem examination. recovery is the most important determinant of survival. 437,444
419
These points notwithstanding, the current experience argues strongly There are several published guidelines for the treatment of invasive
for institution of early treatment based on the “possibility” of invasive mold infections. 445-447 Voriconazole remains the agent of choice for
aspergillosis in subjects at high risk for these infections, rather than primary treatment for invasive aspergillosis. Alternatives including
waiting until the process is classifiable as “probable” or “proven. ” lipid formulations of amphotericin B and the echinocandins are also
Molds are ubiquitous in the environment 293,403,420 and present in a recommended. Primary combination antifungal therapy is not recom-
wide variety of natural and synthetic materials such as soil, decaying mended at this time, given the lack of prospective randomized clinical
vegetation, fireproofing materials, water, and air. Aspergillus trial evidence of efficacy. A recent randomized, double-blinded trial of
423
422
421
species frequently have been detected in the air of hospital rooms, par- treatment of invasive aspergillosis with voriconozole plus anidulafungin
ticularly during construction and renovation. 424,425 Use of specialized versus voriconazole plus placebo in HSCT recipients or patients with
section05_c61-73.indd 620 1/23/2015 12:48:11 PM