Page 203 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 203
ECA3 7/18/06 6:45 PM Page 188
188 The upper limb
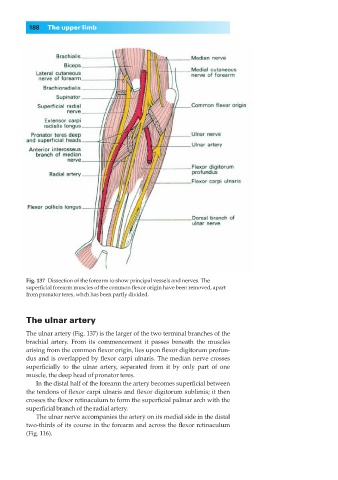
Fig. 137◊Dissection of the forearm to show principal vessels and nerves. The
superficial forearm muscles of the common flexor origin have been removed, apart
from pronator teres, whch has been partly divided.
The ulnar artery
The ulnar artery (Fig. 137) is the larger of the two terminal branches of the
brachial artery. From its commencement it passes beneath the muscles
arising from the common flexor origin, lies upon flexor digitorum profun-
dus and is overlapped by flexor carpi ulnaris. The median nerve crosses
superficially to the ulnar artery, separated from it by only part of one
muscle, the deep head of pronator teres.
In the distal half of the forearm the artery becomes superficial between
the tendons of flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum sublimis; it then
crosses the flexor retinaculum to form the superficial palmar arch with the
superficial branch of the radial artery.
The ulnar nerve accompanies the artery on its medial side in the distal
two-thirds of its course in the forearm and across the flexor retinaculum
(Fig. 116).