Page 20 - Critical Care Notes
P. 20
4223_Tab01_001-044 29/08/14 10:46 AM Page 14
BASICS
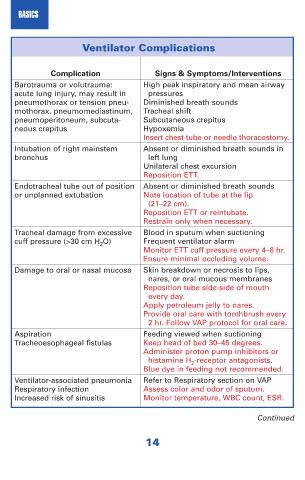
Ventilator Complications
Complication Signs & Symptoms/Interventions
Barotrauma or volutrauma: High peak inspiratory and mean airway
acute lung injury, may result in pressures
pneumothorax or tension pneu- Diminished breath sounds
mothorax, pneumomediastinum, Tracheal shift
pneumoperitoneum, subcuta- Subcutaneous crepitus
neous crepitus Hypoxemia
Insert chest tube or needle thoracostomy.
Intubation of right mainstem Absent or diminished breath sounds in
bronchus left lung
Unilateral chest excursion
Reposition ETT.
Endotracheal tube out of position Absent or diminished breath sounds
or unplanned extubation Note location of tube at the lip
(21–22 cm).
Reposition ETT or reintubate.
Restrain only when necessary.
Tracheal damage from excessive Blood in sputum when suctioning
cuff pressure (>30 cm H 2 O) Frequent ventilator alarm
Monitor ETT cuff pressure every 4–8 hr.
Ensure minimal occluding volume.
Damage to oral or nasal mucosa Skin breakdown or necrosis to lips,
nares, or oral mucous membranes
Reposition tube side-side of mouth
every day.
Apply petroleum jelly to nares.
Provide oral care with toothbrush every
2 hr. Follow VAP protocol for oral care.
Aspiration Feeding viewed when suctioning
Tracheoesophageal fistulas Keep head of bed 30–45 degrees.
Administer proton pump inhibitors or
histamine H 2 -receptor antagonists.
Blue dye in feeding not recommended.
Ventilator-associated pneumonia Refer to Respiratory section on VAP
Respiratory infection Assess color and odor of sputum.
Increased risk of sinusitis Monitor temperature, WBC count, ESR.
Continued
14