Page 55 - Critical Care Notes
P. 55
4223_Tab02_045-106 29/08/14 10:00 AM Page 49
49
Discomfort may be accompanied by weakness, dyspnea, diaphoresis, or anx-
iety; not relieved by NTG. Women may experience atypical discomfort, SOB, or
fatigue. Diabetic patients may not display classic signs and symptoms of AMI.
Elderly patients may experience SOB, pulmonary edema, dizziness, altered
mental status.
ST-segment elevation MI: Look for tall positive T waves and ST-segment ele-
vation of 1 mm or more above baseline.
Non–ST-segment elevation MI: May include ST-segment depression and
T-wave inversion.
Diagnostic Tests
■ ECG findings.
■ Cardiac markers (CK, myoglobin, and troponins).
■ Ischemia modified albumin (IMA): measures changes in serum albumin
when in contact with ischemic tissue. IMA rises faster than other cardiac
enzymes.
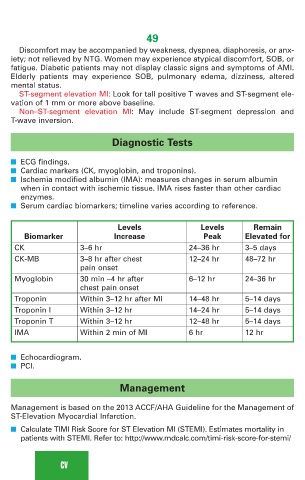
■ Serum cardiac biomarkers; timeline varies according to reference.
Levels Levels Remain
Biomarker Increase Peak Elevated for
CK 3–6 hr 24–36 hr 3–5 days
CK-MB 3–8 hr after chest 12–24 hr 48–72 hr
pain onset
Myoglobin 30 min –4 hr after 6–12 hr 24–36 hr
chest pain onset
Troponin Within 3–12 hr after MI 14–48 hr 5–14 days
Troponin I Within 3–12 hr 14–24 hr 5–14 days
Troponin T Within 3–12 hr 12–48 hr 5–14 days
IMA Within 2 min of MI 6 hr 12 hr
■ Echocardiogram.
■ PCI.
Management
Management is based on the 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of
ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction.
■ Calculate TIMI Risk Score for ST Elevation MI (STEMI). Estimates mortality in
patients with STEMI. Refer to: http://www.mdcalc.com/timi-risk-score-for-stemi/
CV