Page 99 - Critical Care Notes
P. 99
4223_Tab02_045-106 29/08/14 10:00 AM Page 93
93
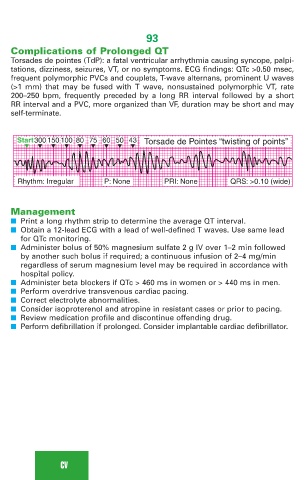
Complications of Prolonged QT
Torsades de pointes (TdP): a fatal ventricular arrhythmia causing syncope, palpi-
tations, dizziness, seizures, VT, or no symptoms. ECG findings: QTc >0.50 msec,
frequent polymorphic PVCs and couplets, T-wave alternans, prominent U waves
(>1 mm) that may be fused with T wave, nonsustained polymorphic VT, rate
200–250 bpm, frequently preceded by a long RR interval followed by a short
RR interval and a PVC, more organized than VF, duration may be short and may
self-terminate.
Start300 150 100 80 75 60 50 43 Torsade de Pointes “twisting of points”
Rhythm: Irregular P: None PRI: None QRS: >0.10 (wide)
Management
■ Print a long rhythm strip to determine the average QT interval.
■ Obtain a 12-lead ECG with a lead of well-defined T waves. Use same lead
for QTc monitoring.
■ Administer bolus of 50% magnesium sulfate 2 g IV over 1–2 min followed
by another such bolus if required; a continuous infusion of 2–4 mg/min
regardless of serum magnesium level may be required in accordance with
hospital policy.
■ Administer beta blockers if QTc > 460 ms in women or > 440 ms in men.
■ Perform overdrive transvenous cardiac pacing.
■ Correct electrolyte abnormalities.
■ Consider isoproterenol and atropine in resistant cases or prior to pacing.
■ Review medication profile and discontinue offending drug.
■ Perform defibrillation if prolonged. Consider implantable cardiac defibrillator.
CV