Page 516 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 516
482 Chapter 14
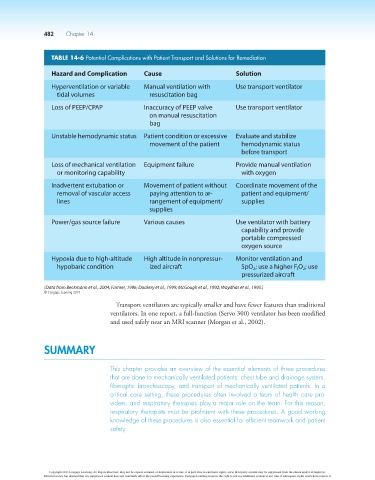
TABLE 14-6 Potential Complications with Patient Transport and Solutions for Remediation
Hazard and Complication Cause Solution
Hyperventilation or variable Manual ventilation with Use transport ventilator
tidal volumes resuscitation bag
Loss of PEEP/CPAP Inaccuracy of PEEP valve Use transport ventilator
on manual resuscitation
bag
Unstable hemodynamic status Patient condition or excessive Evaluate and stabilize
movement of the patient hemodynamic status
before transport
Loss of mechanical ventilation Equipment failure Provide manual ventilation
or monitoring capability with oxygen
Inadvertent extubation or Movement of patient without Coordinate movement of the
removal of vascular access paying attention to ar- patient and equipment/
lines rangement of equipment/ supplies
supplies
Power/gas source failure Various causes Use ventilator with battery
capability and provide
portable compressed
oxygen source
Hypoxia due to high-altitude High altitude in nonpressur- Monitor ventilation and
hypobaric condition ized aircraft SpO ; use a higher F O ; use
I
2
2
pressurized aircraft
(Data from Beckmann et al., 2004; Farmer, 1996; Dockery et al., 1999; McGough et al., 1992; Waydhas et al., 1995.)
© Cengage Learning 2014
Transport ventilators are typically smaller and have fewer features than traditional
ventilators. In one report, a full-function (Servo 300) ventilator has been modified
and used safely near an MRI scanner (Morgan et al., 2002).
SUmmaRy
This chapter provides an overview of the essential elements of three procedures
that are done to mechanically ventilated patients: chest tube and drainage system,
fiberoptic bronchoscopy, and transport of mechanically ventilated patients. In a
critical care setting, these procedures often involved a team of health care pro-
viders, and respiratory therapists play a major role on the team. For this reason,
respiratory therapists must be proficient with these procedures. A good working
knowledge of these procedures is also essential for efficient teamwork and patient
safety.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.