Page 108 - AACN Essentials of Critical-Care Nursing Pocket Handbook, Second Edition
P. 108
Abbreviations: AF, atrial 95
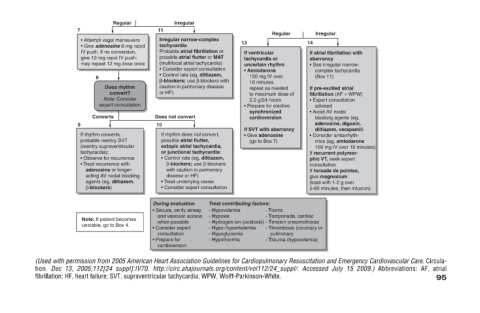
If atrial fibrillation with • See irregular narrow- complex tachycardia If pre-excited atrial fibrillation (AF + WPW) • Expert consultation blocking agents (eg, adenosine, digoxin, diltiazem, verapamil) • Consider antiarrhyth- mics (eg, amiodar
Irregular aberrancy (Box 11) advised • Avoid AV nodal consultation give magnesium
advised 14 - Thrombosis (coronary or
Regular to maximum dose of If SVT with aberrancy - Toxins - Tamponade, cardiac pulmonary - Trauma (hypovolemia)
If ventricular tachycardia or uncertain rhythm • Amiodarone 150 mg IV over 10 minutes repeat as needed 2.2 g/24 hours • Prepare for elective synchronized cardioversion • Give adenosine (go to Box 7) - Hydrogen ion (acidosis) - Tension p
13 Treat contributing factors: - Hypovolemia - Hypoxia - Hypo-/hyperkalemia - Hypoglycemia - Hypothermia (Used with permission from 2005 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emerg
Irregular narrow-complex Probable atrial fibrillation or possible atrial flutter or MAT (multifocal atrial tachycardia) • Consider expert consultation • Control rate (eg, diltiazem, β-blockers; use β-blockers with caution in pulmonary disease If rhythm
Irregular tachycardia Does not convert possible atrial flutter, disease or HF) • Treat underlying cause During evaluation • Secure, verify airway and vascular access
11 or HF) 10 when possible • Consider expert consultation • Prepare for cardioversion fibrillation; HF, heart failure; SVT, supraventricular tachycardia; WPW, Wolff-Parkinson-White.
• Attempt vagal maneuvers • Give adenosine 6-mg rapid IV push. If no conversion, give 12-mg rapid IV push; may repeat 12 mg dose once 8 Converts If rhythm converts. probable reentry SVT (reentry supraventricular • Observe for recurrence • Treat recur
Regular Does rhythm convert? Note: Consider expert consultation
7 9 tachycardia):
tion.