Page 58 - AACN Essentials of Critical-Care Nursing Pocket Handbook, Second Edition
P. 58
Treatment depends on of arrhythmia. ventricular rate. (procainamide, flecainide, channel blockers). usually successful.
Treatment hemodynamic consequences Cardioversion is preferred for markedly reduced cardiac Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers are used to slow Procainamide, flecainide, amiodarone, ibutilide, dofetilide, sotalol may convert to sinus. Use d
• • output. • • • •
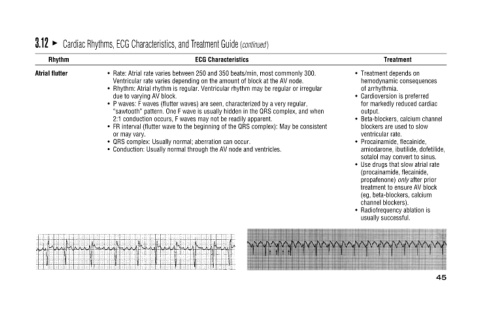
Cardiac Rhythms, ECG Characteristics, and Treatment Guide (continued)
ECG Characteristics Rate: Atrial rate varies between 250 and 350 beats/min, most commonly 300. Ventricular rate varies depending on the amount of block at the AV node. Rhythm: Atrial rhythm is regular. Ventricular rhythm may be regular or irregular P
due to varying AV block. or may vary. QRS complex: Usually normal; aberration can occur.
• • • • • •
Rhythm
Atrial flutter
3.12