Page 59 - AACN Essentials of Critical-Care Nursing Pocket Handbook, Second Edition
P. 59
46
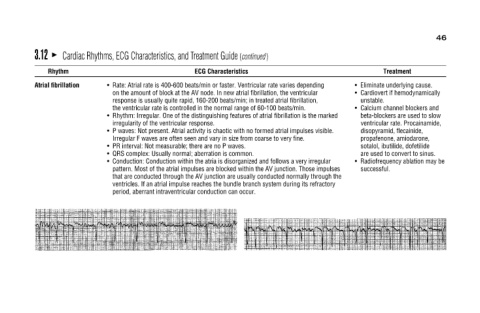
Eliminate underlying cause. disopyramid, flecainide, propafenone, amiodarone, sotalol, ibutilide, dofetilide
Treatment Cardiovert if hemodynamically Calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers are used to slow ventricular rate. Procainamide, are used to convert to sinus. Radiofrequency ablation may be
• • unstable. • • successful.
Cardiac Rhythms, ECG Characteristics, and Treatment Guide (continued)
ECG Characteristics Rate: Atrial rate is 400-600 beats/min or faster. Ventricular rate varies depending on the amount of block at the AV node. In new atrial fibrillation, the ventricular response is usually quite rapid, 160-200 beats/min; in treated
irregularity of the ventricular response. PR interval: Not measurable; there are no P waves. QRS complex: Usually normal; aberration is common. period, aberrant intraventricular conduction can occur.
• • • • • •
Rhythm
Atrial fibrillation
3.12