Page 573 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 573
7-5
p53
54.
qxd
54.
49
e 5
Apt
ara
49
M
9 A
P
g
P
9/0
0
9/2
8:2
009
K34
0-c
23_
K34
LWB K34 0-c 23_ p53 7-5 54. qxd 0 9/0 9/2 009 0 0 8:2 9 A M P a a g e 5 49 Apt ara
L L LWB
LWBK340-c23_23_p537-554.qxd 09/09/2009 08:29 AM Page 549 Aptara
C HAPTER 2 3 / Interventional Cardiology Techniques: Percutaneous Coronary Intervention 549
A B C
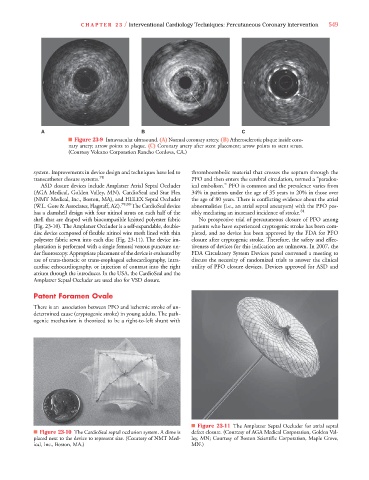
■ Figure 23-9 Intravascular ultrasound. (A) Normal coronary artery. (B) Atherosclerotic plaque inside coro-
nary artery; arrow points to plaque. (C) Coronary artery after stent placement; arrow points to stent struts.
(Courtesy Volcano Corporation Rancho Cordova, CA.)
system. Improvements in device design and techniques have led to thromboembolic material that crosses the septum through the
transcatheter closure systems. 78 PFO and then enters the cerebral circulation, termed a “paradox-
ASD closure devices include Amplatzer Atrial Septal Occluder ical embolism.” PFO is common and the prevalence varies from
(AGA Medical, Golden Valley, MN), CardioSeal and Star Flex 34% in patients under the age of 35 years to 20% in those over
(NMT Medical, Inc., Boston, MA), and HELEX Septal Occluder the age of 80 years. There is conflicting evidence about the atrial
(W.L. Gore & Associates, Flagstaff, AZ). 79,80 The CardioSeal device abnormalities (i.e., an atrial septal aneurysm) with the PFO pos-
has a clamshell design with four nitinol struts on each half of the sibly mediating an increased incidence of stroke. 81
shell that are draped with biocompatible knitted polyester fabric No prospective trial of percutaneous closure of PFO among
(Fig. 23-10). The Amplatzer Occluder is a self-expandable, double- patients who have experienced cryptogenic stroke has been com-
disc device composed of flexible nitinol wire mesh lined with thin pleted, and no device has been approved by the FDA for PFO
polyester fabric sewn into each disc (Fig. 23-11). The device im- closure after cryptogenic stroke. Therefore, the safety and effec-
plantation is performed with a single femoral venous puncture un- tiveness of devices for this indication are unknown. In 2007, the
der fluoroscopy. Appropriate placement of the device is evaluated by FDA Circulatory System Devices panel convened a meeting to
use of trans-thoracic or trans-esophageal echocardiography, intra- discuss the necessity of randomized trials to answer the clinical
cardiac echocardiography, or injection of contrast into the right utility of PFO closure devices. Devices approved for ASD and
atrium through the introducer. In the USA, the CardioSeal and the
Amplatzer Septal Occluder are used also for VSD closure.
Patent Foramen Ovale
There is an association between PFO and ischemic stroke of un-
determined cause (cryptogenic stroke) in young adults. The path-
ogenic mechanism is theorized to be a right-to-left shunt with
■ Figure 23-11 The Amplatzer Septal Occluder for atrial septal
■ Figure 23-10 The CardioSeal septal occlusion system. A dime is defect closure. (Courtesy of AGA Medical Corporation, Golden Val-
placed next to the device to represent size. (Courtesy of NMT Med- ley, MN; Courtesy of Boston Scientific Corporation, Maple Grove,
ical, Inc., Boston, MA.) MN.)