Page 161 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 161
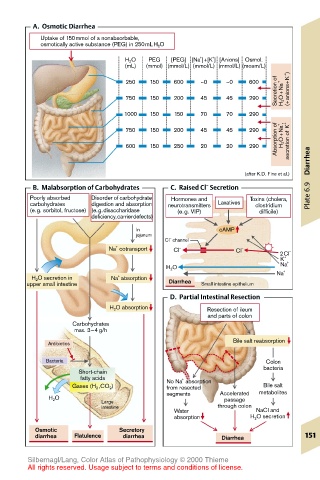
A. Osmotic Diarrhea
Uptake of 150mmol of a nonabsorbable,
osmotically active substance (PEG) in 250mLH 2 O
+
+
H 2 O PEG [PEG] [Na ]+[ K ] [Anions] Osmol.
(mL) (mmol) (mmol/L) (mmol/L) (mmol/L) (mosm/L)
Secretion of H 2 O+Na + (+anions+K + )
250 150 600 ~0 ~0 600
750 150 200 45 45 290
1000 150 150 70 70 290
Absorption of H 2 O+Na + , secretion of K +
750 150 200 45 45 290
600 150 250 20 20 290
(after K.D. Fine et al.) Diarrhea
–
B. Malabsorption of Carbohydrates C. Raised Cl Secretion
Poorly absorbed Disorder of carbohydrate Hormones and Toxins (cholera, Plate 6.9
carbohydrates digestion and absorption neurotransmitters Laxatives clostridium
(e.g. sorbitol, fructose) (e.g.disaccharidase (e.g. VIP) difficile)
deficiency,carrierdefects)
In cAMP
jejunum
–
Cl channel
+
Na cotransport Cl – Cl – 2Cl –
K + +
H 2 O Na
Na +
+
H 2 O secretion in Na absorption
upper small intestine Diarrhea Small intestine epithelium
D. Partial Intestinal Resection
H 2 O absorption Resection of ileum
and parts of colon
Carbohydrates
max. 3–4 g/h
Antibiotics Bile salt reabsorption
Bacteria Colon
bacteria
Short-chain
fatty acids No Na absorption
+
Gases (H 2 ,CO 2 ) from resected Bile salt
segments Accelerated metabolites
H 2 O passage
Large
intestine through colon
Water NaCl and
absorption H 2 O secretion
Osmotic Secretory
diarrhea Flatulence diarrhea Diarrhea 151
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.