Page 1300 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1300
1146 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
1.0 Occasionally, patients with PMF after allogeneic transplant can
experience relapse of their underlying disease, failure of engraftment,
Age ≤55 years or graft failure. Relapse can frequently be treated with donor lym-
Probability of overall survival 0.6 Age >55 years infusions or experience difficulty with engraftment or late graft
0.8
phocyte infusions. Second RIC allogeneic transplants should be
considered for individuals who do not respond to donor lymphocyte
failure. In JAK2V617F-positive patients, monitoring allele burden
following SCT can help predict patients at risk for relapse and prompt
early intervention. The feasibility of utilizing aSCT as the front-line
0.4
therapy for all intermediate- and high-risk patients is limited by the
presence of competing comorbidities or a poor performance status
0.2
due to the systemic effects of the underlying PMF. Although the
JAK2 inhibitors are largely palliative, they do reduce the degree of
splenomegaly and often improve the performance status of such
0.0 patients, frequently resulting in weight gain, and improve their
candidacy for transplant. The reported outcomes with JAK2 inhibitor
0.0 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0 therapy as a component of the conditioning regimen for allogeneic
A Months after transplantation transplantation have resulted in conflicting results, and will require
rigorous testing to determine its effect on immediate and long-term
1.0 survival and transplant-related complications. This approach is cur-
rently being evaluated within the MPD-RC as a phase II trial of
preconditioning ruxolitinib treatment (MPD-RC 114).
Related donor
Probability of overall survival 0.6 MUD ditioning regimens and supportive therapy make this a viable first-line
The fact that allogeneic RIC transplant is curative in appropriate
0.8
patients is undeniable, and the improvements in the design of con-
approach for individuals with HLA-matched donors and advanced
disease. Whether such an approach should also be implemented in
patients with earlier phases of the disease is a point of contention that
0.4
requires further careful investigation. This decision is especially
MMUD
important in young patients with early forms of PMF because their
disease is likely to eventually progress, and the best results with
0.2
allogeneic transplant have been reported in lower risk patients,
especially if they do not have a related donor. The flaw in the argu-
0.0 ment to proceed with immediate transplant in young patients with
early PMF is the exposure to significant mortality and morbidity in
0.0 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0 a patient population that frequently can anticipate a decade or more
B Months after transplantation of a good-quality life with no or minimal therapeutic interventions.
New molecular markers such as JAK2V617F, EZH2, ASXL1, and
CALR mutations will help further refine risk stratification and likely
1.0 Low risk better guide treatment decision.
Many unresolved issues remain to be clarified concerning the
optimal strategy for aSCT in PMF. The need for splenectomy before
Intermediate risk
Probability of overall survival 0.6 High risk results in faster hematopoietic recovery but at the cost of potentially
0.8
aSCT remains a major issue. Splenectomy before aHSCT in PMF
prolonged and complicated postoperative recovery. Although some
analyses suggest improved survival with pretransplant splenectomy, it
has also been associated with a potential increased risk of relapse.
0.4
Moreover, even extensive splenomegaly (>30-cm longitudinal size by
computed tomography scan) does not appear to prolong hematologic
reconstitution after transplant.
0.2
The establishment of valid complete remission criteria of PMF
for response after aSCT are often influenced by GVHD, infections,
0.0 after aSCT remains a major issue because the conventional criteria
or poor graft function, and cannot be used. Conversely, normal blood
0.0 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0 counts and disappearance of disease-related symptoms do not exclude
C Months after transplantation residual disease. In JAK2V617F-positive patients, the mutational
allele burden following transplantation may serve as a surrogate
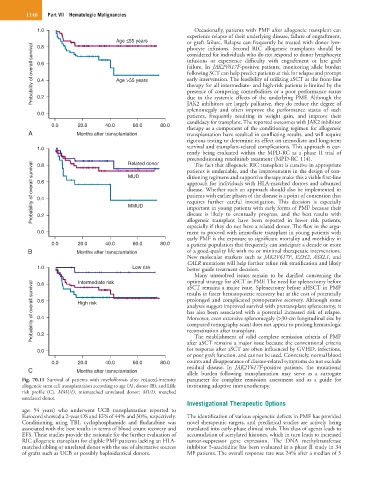
Fig. 70.11 Survival of patients with myelofibrosis after reduced-intensity parameter for complete remission assessment and as a guide for
allogeneic stem cell transplantation according to age (A), donor (B), and Lille instituting adoptive immunotherapy.
risk profile (C). MMUD, mismatched unrelated donor; MUD, matched
unrelated donor.
Investigational Therapeutic Options
age: 54 years) who underwent UCB transplantation reported to
Eurocord showed a 2-year OS and EFS of 44% and 30%, respectively. The identification of various epigenetic defects in PMF has provided
Conditioning using TBI, cyclophosphamide and fludarabine was novel therapeutic targets, and preclinical studies are actively being
associated with the best results in terms of blood count recovery and translated into early-phase clinical trials. This class of agents leads to
EFS. These studies provide the rationale for the further evaluation of accumulation of acetylated histones, which in turn leads to increased
RIC allogeneic transplant for eligible PMF patients lacking an HLA- tumor-suppressor gene expression. The DNA methyltransferase
matched sibling or unrelated donor with the use of alternative sources inhibitor 5-azacitidine has been evaluated in a phase II study in 34
of grafts such as UCB or possibly haploidentical donors. MF patients. The overall response rate was 24% after a median of 5