Page 1756 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1756
1560 Part IX Cell-Based Therapies
Ciclosporin
Prednisolone
Methylprednisolone
PUVA
Infliximab and
daclizumab
MSC MSC
400 2 × 10 /kg 1 × 10 /kg Bilirubin 25
6
6
Bilirubin concentration (mmol/L) 250 15 Number of stools per day
350
20
Stools
300
200
10
150
100
5
50
0
0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 0
Days after ASCT
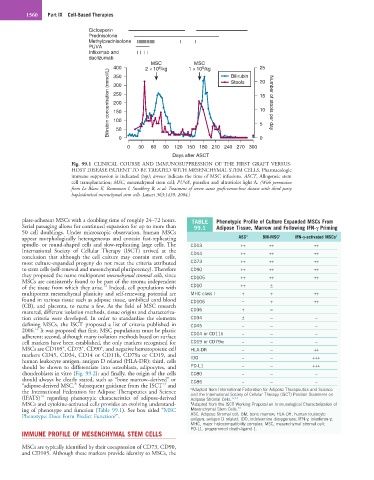
Fig. 99.1 CLINICAL COURSE AND IMMUNOSUPPRESSION OF THE FIRST GRAFT VERSUS-
HOST DISEASE PATIENT TO BE TREATED WITH MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS. Pharmacologic
immune suppression is indicated (top); arrows indicate the time of MSC infusions. ASCT, Allogeneic stem
cell transplantation; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; PUVA, psoralen and ultraviolet light A. (With permission
from Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, et al: Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party
haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet 363:1439, 2004.)
plate-adherent MSCs with a doubling time of roughly 24–72 hours. TABLE Phenotypic Profile of Culture Expanded MSCs From
Serial passaging allows for continued expansion for up to more than 99.1 Adipose Tissue, Marrow and Following IFN-γ Priming
50 cell doublings. Under microscopic observation, human MSCs
appear morphologically heterogeneous and contain fast-replicating ASC a BM-MSC a IFN-γ-activated MSCs b
spindle- or round-shaped cells and slow-replicating large cells. The CD13 ++ ++ ++
International Society of Cellular Therapy (ISCT) arrived at the CD44 ++ ++ ++
conclusion that although the cell culture may contain stem cells,
most culture-expanded progeny do not meet the criteria attributed CD73 ++ ++ ++
to stem cells (self-renewal and mesenchymal pluripotency). Therefore CD90 ++ ++ ++
they proposed the name multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells, since CD105 ++ ++ ++
MSCs are consistently found to be part of the stroma independent
12
of the tissue from which they arise. Indeed, cell populations with CD10 ++ ±
multipotent mesenchymal plasticity and self-renewing potential are MHC class I + + ++
found in various tissue such as adipose tissue, umbilical cord blood CD106 − + ++
(CB), and placenta, to name a few. As the field of MSC research
matured, different isolation methods, tissue origins and characteriza- CD36 + −
tion criteria were developed. In order to standardize the elements CD34 ± − −
defining MSCs, the ISCT proposed a list of criteria published in CD45 − − −
12
2006. It was proposed that first, MSC populations must be plastic − − −
adherent; second, although many isolation methods based on surface CD14 or CD11b
cell markers have been established, the only markers recognized for CD19 or CD79α − − −
+
+
+
MSCs are CD105 , CD73 , CD90 , and negative hematopoietic cell HLA-DR − − ++
markers CD45, CD34, CD14 or CD11b, CD79a or CD19, and IDO − − +++
human leukocyte antigen, antigen D related (HLA-DR); third, cells
should be shown to differentiate into osteoblasts, adipocytes, and PD-L1 − − +++
chondroblasts in vitro (Fig. 99.2); and finally, the origin of the cells CD80 − − −
should always be clearly stated, such as “bone marrow–derived” or CD86 − − −
13
“adipose-derived MSC.” Subsequent guidance from the ISCT and a
Adapted from International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science
the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science and the International Society of Cellular Therapy (ISCT) Position Statement on
14
(IFATS) regarding phenotypic characteristics of adipose-derived Adipose Stromal Cells. 12,14
MSCs and cytokine-activated cells provides an evolving understand- b Adapted from the ISCT Working Proposal on Immunological Characterization of
ing of phenotype and function (Table 99.1). See box titled “MSC Mesenchymal Stem Cells. 13
Phenotype: Does Form Predict Function?”. ASC, Adipose Stromal cell; BM, bone marrow; HLA-DR, human leukocyte
antigen, antigen D related; IDO, indoleamine dioxygenase; IFN-γ, interferon-γ;
MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MSC, mesenchymal stromal cell;
PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1.
IMMUNE PROFILE OF MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS
MSCs are typically identified by their coexpression of CD73, CD90,
and CD105. Although these markers provide identity to MSCs, the