Page 2038 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2038
Chapter 120 Transfusion-Transmitted Diseases 1809
DOLLARS PER QUALITY-ADJUSTED LIFE-YEAR (QALY) TABLE Patients Benefiting From Cytomegalovirus Risk–
120.2 Reduced Blood Components a
Infants <1200 g with CMV-seronegative mothers
Seronegative autologous and allogeneic (CMV-seronegative donors) stem
cell transplant recipients
$100,000
$10,000
$1,000,000
$100,000,000
$10,000,000
Seronegative stem cell transplant candidates
1983 Revised HIV risk behavior donor criteria Seronegative recipients of seronegative solid organ transplants
1984 Seronegative pregnant women
Fetuses receiving intrauterine transfusions
1985 HIV serotesting
Immunosuppressed patients receiving granulocyte transfusions
1986 HIV-seropositive/CMV-seronegative patients
1987 Non-A, non-B serotesting (ALT, anti-HBc) a CMV risk–reduced components include CMV-seronegative and leukocyte-
reduced components.
1988 HLTV seroscreening CMV, Cytomegalovirus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
1989
Cytomegalovirus
1990 HCV seroscreening
CMV, a betaherpesvirus, infects a wide range of cell types, including
leukocytes of the monocyte-macrophage lineage and their progeni-
1991 tors. In the United States, in the population-based National Health
1992 and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III study, 58.9% of
individuals more than 5 years old were seropositive, indicating prior
1993
CMV infection. Prevalence increases with age and is dependent on
1994 race/ethnicity and other demographic factors. The prevention of
1995 transfusion-transmitted CMV infection has depended on the use of
“CMV safe” blood including a combination of leukoreduced and
1996 HIV p24 antigen testing needs cost effectiveness CMV-seronegative blood. There is, however, some evidence that
1997 acute infection may result in plasma viremia and thus the potential
for transfusion infectivity.
1998 Primary CMV infection in immunocompetent individuals is
usually community acquired, often asymptomatic or associated with
1999 HIV and HCV NAT a mild, self-limited infectious mononucleosis syndrome. After virtu-
(p24 antigen testing discontinued) ally all infections, latent virus persists permanently in cellular reser-
voirs, allowing lifelong reactivation, and in the setting of transfusion
2000 or transplantation, the potential for viral transmission via nonleuko-
reduced cellular blood products, and allografts.
2001 In immunosuppressed patients, CMV infection can cause severe
2002 morbidity and mortality from pneumonitis, hepatitis, gastroenteritis,
West Nile virus NAT retinitis, and other inflammatory conditions. CMV infection in low-
2003 platelets bacterial testing birth-weight infants is associated with sepsis-like syndromes, respira-
tory distress, and liver and bone marrow dysfunction. Their infections
2004 can be acquired in utero, from breast milk, or from transfusion.
2005 Reported infant morbidity varies considerably but can approach 50%
of seronegative low-birth-weight infants receiving unscreened, non-
2006 leukoreduced blood. CMV-seronegative marrow transplant patients
2007 T. cruzi serotesting (all donors) are also susceptible to CMV infection; but the adoption of routine
monitoring for CMV antigen or nucleic acid in transplant recipients
2008
and of preemptive antiviral therapy have decreased this risk. Sero-
2009 T. cruzi serotesting (first-time donors only) negative solid organ transplant recipients are also susceptible to
2010 Minipool HIV/HCV/HBV NAT symptomatic transfusion-transmitted CMV infections. CMV-
seronegative, HIV-infected patients are another group at risk for
transfusion-transmitted primary CMV infection. The historical risk
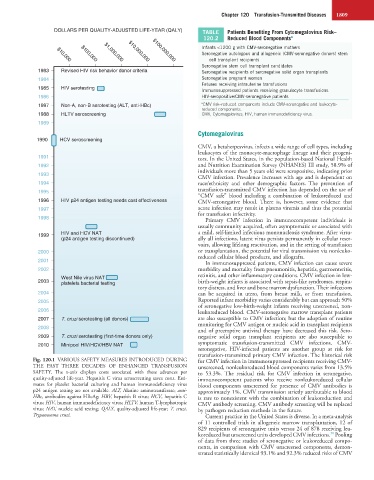
Fig. 120.1 VARIOUS SAFETY MEASURES INTRODUCED DURING for CMV infection in immunosuppressed recipients receiving CMV-
THE PAST THREE DECADES OF ENHANCED TRANSFUSION unscreened, nonleukoreduced blood components varies from 13.5%
SAFETY. The x-axis displays costs associated with these advances per to 53.3%. The residual risk for CMV infection in seronegative,
quality-adjusted life-year. Hepatitis C virus seroscreening saves costs. Esti- immunocompetent patients who receive nonleukoreduced cellular
mates for platelet bacterial culturing and human immunodeficiency virus blood components unscreened for presence of CMV antibodies is
p24 antigen testing are not available. ALT, Alanine aminotransferase; anti- approximately 1%. CMV transmission strictly attributable to blood
HBc, antibodies against HBcAg; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C is rare to nonexistent with the combination of leukoreduction and
virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HLTV, human T-lymphotropic CMV antibody screening. CMV antibody screening will be replaced
virus; NAT, nucleic acid testing; QALY, quality-adjusted life-year; T. cruzi, by pathogen reduction methods in the future.
Trypanosoma cruzi. Current practice in the United States is diverse. In a meta-analysis
of 11 controlled trials in allogeneic marrow transplantation, 12 of
829 recipients of seronegative units versus 24 of 878 receiving leu-
30
koreduced but unscreened units developed CMV infections. Pooling
of data from three studies of seronegative or leukoreduced compo-
nents, in comparison with CMV unscreened components, demon-
strated statistically identical 93.1% and 92.3% reduced risks of CMV