Page 2033 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2033
1804 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
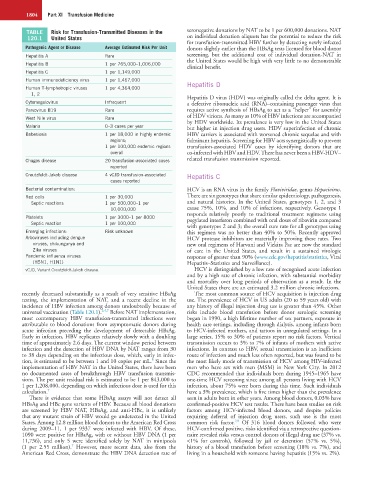
TABLE Risk for Transfusion-Transmitted Diseases in the seronegative donations by NAT to be 1 per 600,000 donations. NAT
120.1 United States on individual donation aliquots has the potential to reduce the risk
for transfusion-transmitted HBV further by detecting newly infected
Pathogenic Agent or Disease Average Estimated Risk Per Unit donors slightly earlier than the HBsAg tests licensed for blood donor
Hepatitis A Rare screening, but the additional cost of individual donation-NAT in
the United States would be high with very little to no demonstrable
Hepatitis B 1 per 765,000–1,006,000
clinical benefit.
Hepatitis C 1 per 1,149,000
Human immunodeficiency virus 1 per 1,467,000
Human T-lymphotropic viruses 1 per 4,364,000 Hepatitis D
1, 2
Hepatitis D virus (HDV) was originally called the delta agent. It is
Cytomegalovirus Infrequent a defective ribonucleic acid (RNA)–containing passenger virus that
Parvovirus B19 Rare requires active synthesis of HBsAg to act as a “helper” for assembly
West Nile virus Rare of HDV virions. As many as 10% of HBV infections are accompanied
by HDV worldwide. Its prevalence is very low in the United States
Malaria 0–3 cases per year but higher in injection drug users. HDV superinfection of chronic
Babesiosis 1 per 18,000 in highly endemic HBV carriers is associated with worsened chronic sequelae and with
regions; fulminant hepatitis. Screening for HBV acts synergistically to prevent
1 per 100,000 endemic regions transfusion-associated HDV cases by identifying donors that are
overall co-infected with HBV and HDV. There has never been a HBV-HDV–
Chagas disease 20 transfusion-associated cases related transfusion transmission reported.
reported
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease 4 vCJD transfusion-associated Hepatitis C
cases reported
Bacterial contamination: HCV is an RNA virus in the family Flaviviridae, genus Hepacivirus.
Red cells 1 per 30,000 There are six genotypes that share similar epidemiology, pathogenesis,
Septic reactions 1 per 500,000–1 per and natural histories. In the United States, genotypes 1, 2, and 3
10,000,000 cause 75%, 10%, and 10% of infections, respectively. Genotype 1
responds relatively poorly to traditional treatment regimens using
Platelets 1 per 3000–1 per 8000 pegylated interferon combined with oral doses of ribavirin compared
Septic reaction 1 per 100,000
with genotypes 2 and 3; the overall cure rate for all genotypes using
Emerging infections: Risk unknown this regimen was no better than 40% to 50%. Recently approved
Arboviruses including dengue HCV protease inhibitors are materially improving these rates. Two
viruses, chikungunya and new oral regimens of Harvoni and Viekira Pac are now the standard
Zika viruses of care in the United States, and result in a sustained virologic
Pandemic influenza viruses response of greater than 90% (www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics, Viral
(H5N1, H1N1) Hepatitis–Statistics and Surveillance).
vCJD, Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. HCV is distinguished by a low rate of recognized acute infection
and by a high rate of chronic infection, with substantial morbidity
and mortality over long periods of observation as a result. In the
United States there are an estimated 3.2 million chronic infections.
recently decreased substantially as a result of very sensitive HBsAg The most common source of HCV acquisition is injection drug
testing, the implementation of NAT, and a recent decline in the use. The prevalence of HCV in US adults (20 to 59 years old) with
incidence of HBV infection among donors undoubtedly because of any history of illegal injection drug use is greater than 45%. Other
universal vaccination (Table 120.1). 3,4,7 Before NAT implementation, risks include blood transfusion before donor serologic screening
most contemporary HBV transfusion-transmitted infections were began in 1990, a high lifetime number of sex partners, exposure in
attributable to blood donations from asymptomatic donors during health care settings, including through dialysis, among infants born
acute infection preceding the development of detectable HBsAg. to HCV-infected mothers, and tattoos in unregulated settings. In a
Early in infection, HBV replicates relatively slowly with a doubling large series, 15% to 30% of patients report no risk factors. Vertical
time of approximately 2.6 days. The current window period between transmission occurs to 3% to 7% of infants of mothers with active
infection and the detection of HBV DNA by NAT ranges from 30 infections. In contrast to HBV, sexual transmission is an inefficient
to 38 days depending on the infectious dose, which, early in infec- route of infection and much less often reported, but was found to be
8
tion, is estimated to be between 1 and 10 copies per mL. Since the the most likely mode of transmission of HCV among HIV-infected
implementation of HBV NAT in the United States, there have been men who have sex with men (MSM) in New York City. In 2012
no documented cases of breakthrough HBV transfusion transmis- CDC recommended that individuals born during 1945–1965 have
sions. The per unit residual risk is estimated to be 1 per 843,000 to one-time HCV screening since among all persons living with HCV
1 per 1,208,000, depending on which infectious dose is used for this infection, about 75% were born during this time. Such individuals
calculation. 7 have a 3% prevalence, which is five times higher than the prevalence
There is evidence that some HBsAg assays will not detect all seen in adults born in other years. Among blood donors, 0.03% have
HBsAg and HBc gene variants of HBV. Because all blood donations confirmed-positive HCV test results. There have been studies on risk
are screened by HBV NAT, HBsAg, and anti-HBc, it is unlikely factors among HCV-infected blood donors, and despite policies
that any mutant strain of HBV would go undetected in the United requiring deferral of injection drug users, such use is the most
2,9
States. Among 12.8 million blood donors to the American Red Cross common risk factor. Of 316 blood donors followed who were
during 2009–11, 1 per 9337 were infected with HBV. Of these, HCV-confirmed positive, risks identified via a retrospective question-
1090 were positive for HBsAg, with or without HBV DNA (1 per naire revealed risks versus control donors of illegal drug use (37% vs.
11,736), and only 5 were identified solely by NAT in minipools <1% for controls), followed by jail or detention (57% vs. 5%),
7
(1 per 2.55 million). However, more recent data, also from the history of a blood transfusion before screening (18% vs. 7%), and
American Red Cross, demonstrate the HBV DNA detection rate of living in a household with someone having hepatitis (15% vs. 2%).