Page 2503 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2503
Chapter 152 Hematologic Manifestations of Childhood Illness 2235
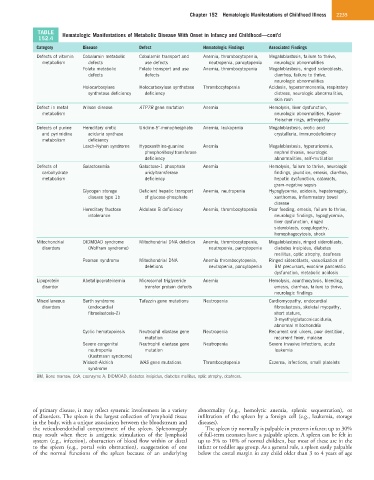
TABLE Hematologic Manifestations of Metabolic Disease With Onset in Infancy and Childhood—cont’d
152.4
Category Disease Defect Hematologic Findings Associated Findings
Defects of vitamin Cobalamin metabolic Cobalamin transport and Anemia, thrombocytopenia, Megaloblastosis, failure to thrive,
metabolism defects use defects neutropenia, pancytopenia neurologic abnormalities
Folate metabolic Folate transport and use Anemia, thrombocytopenia Megaloblastosis, ringed sideroblasts,
defects defects diarrhea, failure to thrive,
neurologic abnormalities
Holocarboxylase Holocarboxylase synthetase Thrombocytopenia Acidosis, hyperammonemia, respiratory
synthetase deficiency deficiency distress, neurologic abnormalities,
skin rash
Defect in metal Wilson disease ATP7B gene mutation Anemia Hemolysis, liver dysfunction,
metabolism neurologic abnormalities, Kayser-
Fleischer rings, arthropathy
Defects of purine Hereditary orotic Uridine-5′-monophosphate Anemia, leukopenia Megaloblastosis, orotic acid
and pyrimidine aciduria synthase crystalluria, immunodeficiency
metabolism deficiency
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Hypoxanthine-guanine Anemia Megaloblastosis, hyperuricemia,
phosphoribosyltransferase nephrolithiasis, neurologic
deficiency abnormalities, self-mutilation
Defects of Galactosemia Galactose-1 phosphate Anemia Hemolysis, failure to thrive, neurologic
carbohydrate uridyltransferase findings, jaundice, emesis, diarrhea,
metabolism deficiency hepatic dysfunction, cataracts,
gram-negative sepsis
Glycogen storage Deficient hepatic transport Anemia, neutropenia Hypoglycemia, acidosis, hepatomegaly,
disease type 1b of glucose-phosphate xanthomas, inflammatory bowel
disease
Hereditary fructose Aldolase B deficiency Anemia, thrombocytopenia Poor feeding, emesis, failure to thrive,
intolerance neurologic findings, hypoglycemia,
liver dysfunction, ringed
sideroblasts, coagulopathy,
hemophagocytosis, shock
Mitochondrial DIDMOAD syndrome Mitochondrial DNA deletion Anemia, thrombocytopenia, Megaloblastosis, ringed sideroblasts,
disorders (Wolfram syndrome) neutropenia, pancytopenia diabetes insipidus, diabetes
mellitus, optic atrophy, deafness
Pearson syndrome Mitochondrial DNA Anemia thrombocytopenia, Ringed sideroblasts, vacuolization of
deletions neutropenia, pancytopenia BM precursors, exocrine pancreatic
dysfunction, metabolic acidosis
Lipoprotein Abetalipoproteinemia Microsomal triglyceride Anemia Hemolysis, acanthocytosis, bleeding,
disorder transfer protein defects emesis, diarrhea, failure to thrive,
neurologic findings
Miscellaneous Barth syndrome Tafazzin gene mutations Neutropenia Cardiomyopathy, endocardial
disorders (endocardial fibroelastosis, skeletal myopathy,
fibroelastosis-2) short stature,
3-myethylglutaconicaciduria,
abnormal mitochondria
Cyclic hematopoiesis Neutrophil elastase gene Neutropenia Recurrent oral ulcers, poor dentition,
mutation recurrent fever, malaise
Severe congenital Neutrophil elastase gene Neutropenia Severe invasive infections, acute
neutropenia mutation leukemia
(Kostmann syndrome)
Wiskott-Aldrich WAS gene mutations Thrombocytopenia Eczema, infections, small platelets
syndrome
BM, Bone marrow; CoA, coenzyme A; DIDMOAD, diabetes insipidus, diabetes mellitus, optic atrophy, deafness.
of primary disease, it may reflect systemic involvement in a variety abnormality (e.g., hemolytic anemia, splenic sequestration), or
of disorders. The spleen is the largest collection of lymphoid tissue infiltration of the spleen by a foreign cell (e.g., leukemia, storage
in the body, with a unique association between the bloodstream and diseases).
the reticuloendothelial compartment of the spleen. Splenomegaly The spleen tip normally is palpable in preterm infants; up to 30%
may result when there is antigenic stimulation of the lymphoid of full-term neonates have a palpable spleen. A spleen can be felt in
system (e.g., infection), obstruction of blood flow within or distal up to 5% to 10% of normal children, but most of these are in the
to the spleen (e.g., portal vein obstruction), exaggeration of one infant or toddler age group. As a general rule, a spleen easily palpable
of the normal functions of the spleen because of an underlying below the costal margin in any child older than 3 to 4 years of age