Page 375 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 375
Chapter 26 Biology of Erythropoiesis, Erythroid Differentiation, and Maturation 311
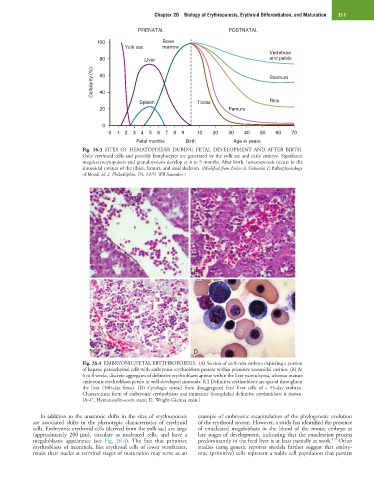
PRENATAL POSTNATAL
100 Bone
Yolk sac marrow
Vertebrae
80 Liver and pelvis
Cellularity (%) 60 Sternum
40
Spleen Tibias Ribs
20 Femurs
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
Fetal months Birth Age in years
Fig. 26.3 SITES OF HEMATOPOIESIS DURING FETAL DEVELOPMENT AND AFTER BIRTH.
Only erythroid cells and possibly lymphocytes are generated by the yolk sac and early embryo. Significant
megakaryocytopoiesis and granulopoiesis develop at 4 to 5 months. After birth, hematopoiesis occurs in the
sinusoidal cavities of the tibias, femurs, and axial skeleton. (Modified from Erslev A, Gabuzda T: Pathophysiology
of blood, ed 2, Philadelphia, PA, 1979, WB Saunders.)
A B
C D
Fig. 26.4 EMBRYONIC/FETAL ERYTHROPOIESIS. (A) Section of an 8-mm embryo depicting a portion
of hepatic parenchymal cells with embryonic erythroblasts present within primitive sinusoidal cavities. (B) At
6 to 8 weeks, discrete aggregates of definitive erythroblasts appear within the liver parenchyma, whereas mature
embryonic erythroblasts persist in well-developed sinusoids. (C) Definitive erythroblasts are spread throughout
the liver (100-day fetus). (D) Cytologic spread from disaggregated fetal liver cells of a 55-day embryo.
Characteristic form of embryonic erythroblasts and immature (basophilic) definitive erythroblasts is shown.
(A–C, Hematoxylin-eosin stain; D, Wright-Giemsa stain.)
In addition to the anatomic shifts in the sites of erythropoiesis example of embryonic recapitulation of the phylogenetic evolution
are associated shifts in the phenotypic characteristics of erythroid of the erythroid system. However, a study has identified the presence
cells. Embryonic erythroid cells (derived from the yolk sac) are large of enucleated megaloblasts in the blood of the mouse embryo at
(approximately 200 µm), circulate as nucleated cells, and have a late stages of development, indicating that the enucleation process
410
megaloblastic appearance (see Fig. 26.4). The fact that primitive predominantly in the fetal liver is at least partially at work. Other
erythroblasts of mammals, like erythroid cells of lower vertebrates, studies using genetic reporter models further suggest that embry-
retain their nuclei at terminal stages of maturation may serve as an onic (primitive) cells represent a stable cell population that persists